Proresolving Mediators LXB4 and RvE1 Regulate Inflammation in Stromal Cells from Patients with Shoulder Tendon Tears
- PMID: 31437425
- PMCID: PMC6876268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.07.011
Proresolving Mediators LXB4 and RvE1 Regulate Inflammation in Stromal Cells from Patients with Shoulder Tendon Tears
Abstract
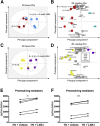
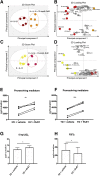
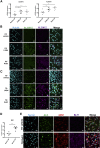
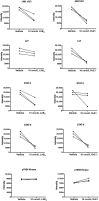
Tendon stromal cells isolated from patients with chronic shoulder rotator cuff tendon tears have dysregulated resolution responses. Current therapies do not address the biological processes concerned with persistent tendon inflammation; therefore, new therapeutic approaches that target tendon stromal cells are required. We examined whether two specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs), lipoxin B4 (LXB4) and resolvin E1 (RvE1), modulate the bioactive lipid mediator profiles of IL-1β-stimulated tendon cells derived from patients with shoulder tendon tears and healthy volunteers. We also examined whether LXB4 or RvE1 treatments moderated the proinflammatory phenotype of tendon tear stromal cells. Incubation of IL-1β-treated patient-derived tendon cells in LXB4 or RvE1 up-regulated concentrations of SPMs. RvE1 treatment of diseased tendon stromal cells increased 15-epi-LXB4 and regulated postaglandin F2α. LXB4 or RvE1 also induced expression of the SPM biosynthetic enzymes 12-lipoxygenase and 15-lipoxygenase. RvE1 treatment up-regulated the proresolving receptor human resolvin E1 compared with vehicle-treated cells. Incubation in LXB4 or RvE1 moderated the proinflammatory phenotype of patient-derived tendon tear cells, regulating markers of tendon inflammation, including podoplanin, CD90, phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, and IL-6. LXB4 and RvE1 counterregulate inflammatory processes in tendon stromal cells, supporting the role of these molecules as potential therapeutics to resolve tendon inflammation.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Bioactive Lipids in Shoulder Tendon Tears.Am J Pathol. 2019 Nov;189(11):2149-2153. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31526772
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carr A.J., Cooper C.D., Campbell M.K., Rees J.L., Moser J., Beard D.J., Fitzpatrick R., Gray A., Dawson J., Murphy J., Bruhn H., Cooper D., Ramsay C.R. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of open and arthroscopic rotator cuff repair [the UK Rotator Cuff Surgery (UKUFF) randomised trial] Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1–218. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dean B.J., Franklin S.L., Murphy R.J., Javaid M.K., Carr A.J. Glucocorticoids induce specific ion-channel-mediated toxicity in human rotator cuff tendon: a mechanism underpinning the ultimately deleterious effect of steroid injection in tendinopathy? Br J Sports Med. 2014;48:1620–1626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

