WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1
- PMID: 31438961
- PMCID: PMC6704583
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1053-8
WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation, a well-known modification with new epigenetic functions, has been reported to participate in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), providing novel insights into the molecular pathogenesis of this disease. However, as the key component of m6A methylation, Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP) has not been well studied in HCC. Here we investigated the biological role and underlying mechanism of WTAP in liver cancer.
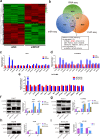
Methods: We determined the expression of WTAP and its correlation with clinicopathological features using tissue microarrays and the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. And we clarified the effects of WTAP on HCC cells using cell proliferation assay, colony formation, Edu assay and subcutaneous xenograft experiments. We then applied RNA sequencing combined with gene expression omnibus (GEO) data to screen candidate targets of WTAP. Finally, we investigated the regulatory mechanism of WTAP in HCC by m6A dot blot assay, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) assay, dual luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay and Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay.
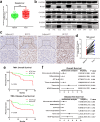
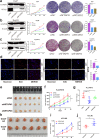
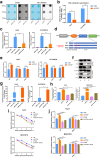
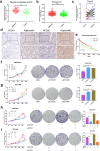
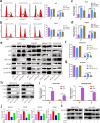
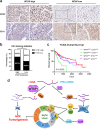
Results: We demonstrated that WTAP was highly expressed in HCC which indicated the poor prognosis, and that WTAP expression served as an independent predictor of HCC survival. Functionally, WTAP promoted the proliferation capability and tumor growth of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, ETS proto-oncogene 1 (ETS1) was identified as the downstream effector of WTAP. The m6A modification regulated by WTAP led to post-transcriptional suppression of ETS1, with the implication of Hu-Antigen R (HuR) as an RNA stabilizer. Then ETS1 was found to inhibit the progression of HCC and could rescue the phenotype induced by WTAP deficiency. Moreover, WTAP modulated the G2/M phase of HCC cells through a p21/p27-dependent pattern mediated by ETS1.
Conclusion: We have identified that WTAP is significantly up-regulated in HCC and promotes liver cancer development. WTAP-guided m6A modification contributes to the progression of HCC via the HuR-ETS1-p21/p27 axis. Our study is the first to report that WTAP-mediated m6A methylation has a crucial role in HCC oncogenesis, and highlights WTAP as a potential therapeutic target of HCC treatment.
Keywords: ETS1; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); N6-methyladenosine (m6A); Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

