Implementation of the Dutch expertise centre for child abuse: descriptive data from the first 4 years
- PMID: 31439611
- PMCID: PMC6707647
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031008
Implementation of the Dutch expertise centre for child abuse: descriptive data from the first 4 years
Abstract
Objective: Combined paediatric and forensic medical expertise to interpret physical findings is not available in Dutch healthcare facilities. The Dutch Expertise Centre for Child Abuse (DECCA) was founded in the conviction that this combination is essential in assessing potential physical child abuse. DECCA is a collaboration between the three paediatric hospitals and the Netherlands Forensic Institute. DECCA works with Bayes' theorem and uses likelihood ratios in their conclusions.
Design: We present the implementation process of DECCA and cross-sectional data of the first 4 years.
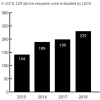
Participants: Between 14 December 2014 and 31 December 2018, a total of 761 advisory requests were referred, all of which were included in this study. An advisee evaluation over the year 2015 was performed using a self-constructed survey to gain insight in the first experiences with DECCA.
Results: 761 cases were included, 381 (50.1%) boys and 361 (47.4%) girls (19 cases (2.5%) sex undisclosed). Median age was 1.5 years (range 1 day to 20 years). Paediatricians (53.1%) and child safeguarding doctors (21.9%) most frequently contacted DECCA. The two most common reasons for referral were presence of injury/skin lesions (n=592) and clinical history inconsistent with findings (n=145). The most common injuries were bruises (264) and non-skull fractures (166). Outcome of DECCA evaluation was almost certainly no or improbable child abuse in 35.7%; child abuse likely or almost certain in 24.3%, and unclear in 12%. The advisee evaluations (response rate 50%) showed that 93% experienced added value and that 100% were (very) satisfied with the advice.
Conclusion: Data show growing interest in the expertise of DECCA through the years. DECCA seems to be a valuable addition to Dutch child protection, since advisee value the service and outcome of DECCA evaluations. In almost half of the cases, DECCA concluded that child abuse could not be substantiated.
Keywords: child protection child abuse forensic medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, et al. . Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The adverse childhood experiences (ACE) study. Am J PrevMed 1998;14:245–58. - PubMed
-
- Gelles RJ, Perlman S. Estimated annual cost of child abuse and neglect. Chicago IL: Prevent Child Abuse America, 2012.
-
- Royal Dutch Medical Association KNMG-meldcode kindermishandeling en huiselijk geweld 2018. Available: https://www.knmg.nl/advies-richtlijnen/knmg-publicaties/meldcode-kinderm...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
