50+ years of eukaryotic transcription: an expanding universe of factors and mechanisms
- PMID: 31439941
- PMCID: PMC6867066
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0287-x
50+ years of eukaryotic transcription: an expanding universe of factors and mechanisms
Abstract
The landmark 1969 discovery of nuclear RNA polymerases I, II and III in diverse eukaryotes represented a major turning point in the field that, with subsequent elucidation of the distinct structures and functions of these enzymes, catalyzed an avalanche of further studies. In this Review, written from a personal and historical perspective, I highlight foundational biochemical studies that led to the discovery of an expanding universe of the components of the transcriptional and regulatory machineries, and a parallel complexity in gene-specific mechanisms that continue to be explored to the present day.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
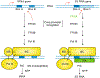
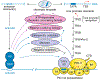
References
-
- Jacob F & Monod J Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol 3, 318–356 (1961). - PubMed
-
- Weiss SB & Gladstone L A mammalian system for the incorporation of cytidine triphosphate into ribonucleic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc 81, 4118–4119 (1959).
-
- Hurwitz J The discovery of RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem 280, 42477–42485 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Burgess RR, Travers AA, Dunn JJ & Bautz EK Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature 221, 43–46 (1969). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

