Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Alarmins and Their Potential Involvement in Bone Homeostasis
- PMID: 31440259
- PMCID: PMC6694442
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01901
Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Alarmins and Their Potential Involvement in Bone Homeostasis
Abstract
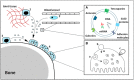
Extracellular vesicles are a heterogeneous group of cell-derived membranous structures, which facilitate intercellular communication. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of extracellular vesicles in bone homeostasis, as mediators of crosstalk between different bone-resident cells. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts are capable of releasing various types of extracellular vesicles that promote both osteogenesis, as well as, osteoclastogenesis, maintaining bone homeostasis. However, the contribution of immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles in bone homeostasis remains largely unknown. Recent proteomic studies showed that alarmins are abundantly present in/on macrophage-derived EVs. In this review we will describe these alarmins in the context of bone matrix regulation and discuss the potential contribution macrophage-derived EVs may have in this process.
Keywords: alarmins; bone homeostasis; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated cholangiocytes release macrophage-polarizing extracellular vesicles bearing the DAMP S100A11.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):C788-C799. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00250.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31365294 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoblast-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Biological Tools for the Delivery of Active Molecules to Bone.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Mar;33(3):517-533. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3332. Epub 2017 Dec 11. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29091316
-
Monocyte-derived extracellular vesicles stimulate cytokine secretion and gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases by mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.FEBS J. 2018 Jun;285(12):2337-2359. doi: 10.1111/febs.14485. Epub 2018 May 18. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29732732
-
Exosomes and Extracellular RNA in Muscle and Bone Aging and Crosstalk.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019 Dec;17(6):548-559. doi: 10.1007/s11914-019-00537-7. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019. PMID: 31741222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in bone homeostasis: key roles of physiological and pathological conditions.J Bone Miner Metab. 2023 May;41(3):345-357. doi: 10.1007/s00774-022-01362-2. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Bone Miner Metab. 2023. PMID: 35943593 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-bone-derived exosomes: a new perspective on regulators of bone homeostasis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 25;22(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01431-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38273356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtopography of Immune Cells in Osteoporosis and Bone Lesions by Endocrine Disruptors.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 2;11:1737. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01737. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the application of framework nucleic acid in bone regeneration.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Dec 1;39(6):624-632. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.06.002. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34859621 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Osteoblasts-derived exosomes as potential novel communicators in particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Aug 6;28:101189. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101189. eCollection 2024 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39221219 Free PMC article.
-
3WJ RNA Nanoparticles-Aptamer Functionalized Exosomes From M2 Macrophages Target BMSCs to Promote the Healing of Bone Fractures.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023 Nov 3;12(11):758-774. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szad052. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37740533 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

