AGER-Mediated Lipid Peroxidation Drives Caspase-11 Inflammasome Activation in Sepsis
- PMID: 31440260
- PMCID: PMC6694796
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01904
AGER-Mediated Lipid Peroxidation Drives Caspase-11 Inflammasome Activation in Sepsis
Abstract
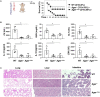
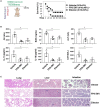
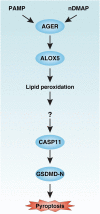
Inflammasome activation can trigger an inflammatory and innate immune response through the release of cytokines and induction of pyroptosis. A dysfunctional inflammasome has been implicated in the development of human pathologies, including sepsis and septic shock. Here, we show that advanced glycosylation end-product specific receptor (AGER/RAGE) is required for caspase-11 inflammasome activation in macrophages. A nuclear damage-associated molecular pattern (nDAMP) complex, including high-mobility group box 1, histone, and DNA, can promote caspase-11-mediated gasdermin D cleavage, interleukin 1β proteolytic maturation, and lactate dehydrogenase release. The inhibition of AGER-mediated lipid peroxidation via arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5) limits caspase-11 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in macrophages in response to nDAMPs or cytosolic lipopolysaccharide. Importantly, the pharmacologic inhibition of the AGER-ALOX5 pathway or global depletion (Ager-/-) or conditional depletion of AGER in myeloid cells (AgerMye-/-) protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced septic death in poly(I:C)-primed mice. These data identify a molecular basis for caspase-11 inflammasome activation and provide a potential strategy to treat sepsis.
Keywords: AGER; ALOX5; DAMP; LPS; caspase-11; inflammasome; lipid peroxidation; sepsis.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

