A novel thiol-dependent serine protease from Neocosmospora sp. N1
- PMID: 31440596
- PMCID: PMC6699422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02246
A novel thiol-dependent serine protease from Neocosmospora sp. N1
Abstract
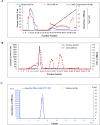
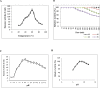
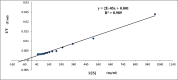
Alkaline proteases have several industrial applications. In the present study, newly isolated Neocosmospora sp. N1 was screened as hyper producer of serine protease. A multimeric protease of the fungus was purified to homogeneity till 96.78 fold purification with 22.51% recovery. The homogeneity of purified enzyme was checked by native PAGE and its molecular weight was found to be 198.03 kDa by MALDI-TOF. On SDS-PAGE analysis, enzyme was found to be a hetero oligomer of 17.66 kDa and 20.89 kDa subunits. The purified enzyme showed maximum activity with casein as substrate at 60 °C and pH 8.5. The Km and Vmax values were found to be 0.015 mg/ml and 454.45 U/ml, respectively. The enzyme was completely inhibited by PMSF, while the activity was 40% enhanced using β-mercaptoethanol, suggesting that it is a thiol-dependent serine protease. The purified protease was active over an alkaline pH range from 7 to 12 and temperatures from 20 °C to 60 °C. The enzyme exhibited excellent stability, almost 100% towards organic solvents such as toluene, benzene and hexane, surfactants such as Triton X-100, Tween-20, Tween-80 and SDS, as well as commercial detergents. The significant properties of purified enzyme assure that it could be a potential candidate for commercial purposes.
Keywords: Biotechnology; Enzyme kinetics; Enzymology; MALDI-TOF; Microbial biotechnology; Microbiology; Serine protease; Superdex 200.
Figures


References
-
- Vojcic L., Pitzler C., Korfer G., Jakob F., Martinez R., Maurer K.H., Schwaneberg U. Advances in protease engineering for laundry detergents. N. Biotech. 2015;32(6):629–634. - PubMed
-
- Elliah P., Srinivasalu B., Adinarayana K. A review on microbial alkaline proteases. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2002;61:690–704.
-
- Jisha V.N., Smitha R.B., Pradeep S., Sreedevi S., Unni K.N., Sajith S., Priji P., Josh M.S., Benjamin S. Versatility of microbial proteases. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2013;1(3):39–51.
-
- Tavano O.L. Protein hydrolysis using proteases: an important tool for food biotechnology. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013;90:1–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

