Wnt status-dependent oncogenic role of BCL9 and BCL9L in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31440992
- PMCID: PMC7220899
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09977-w
Wnt status-dependent oncogenic role of BCL9 and BCL9L in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway is a frequent event in hepatocellular carcinoma and is associated with enhanced cell survival and proliferation. Therefore, targeting this signaling pathway is discussed as an attractive therapeutic approach for HCC treatment. BCL9 and BCL9L, two homologous coactivators of the β-catenin transcription factor complex, have not yet been comprehensively characterized in HCC. We aimed to elucidate the roles of BCL9 and BCL9L, especially regarding Wnt/β-catenin signaling and their prognostic value in HCC.
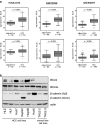
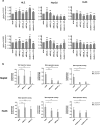
Methods: Expression of BCL9/BCL9L was determined in HCC cell lines (HLE, HLF, Huh7, HepG2, Hep3B, and Huh6) and normal liver cell lines (THLE-2 and THLE-3). To analyze proliferation and apoptosis, BCL9 and/or BCL9L were knocked down in Wnt-inactive HLE and Wnt-active HepG2 and Huh6 cells using siRNA. Subsequently, Wnt reporter assays were performed in HepG2 and Huh6 cells. BCL9 and BCL9L expression, clinicopathological and survival data of public HCC datasets were analyzed, taking the Wnt signaling status into account.
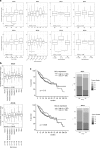
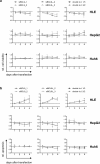
Results: Knockdown of BCL9L, but not of BCL9, reduced Wnt signaling activity. Knockdown of BCL9 and/or BCL9L reduced cell viability and increased apoptosis of Wnt-inactive HCC cells, but had no effect in Wnt-active cells. Expression of BCL9 and BCL9L was upregulated in human HCC and increased with progressing dedifferentiation. For BCL9L, higher expression was observed in tumors of larger size. Overexpression of BCL9 and BCL9L correlated with poor overall survival, especially in HCC without activated Wnt signaling.
Conclusion: Oncogenic BCL9 proteins represent promising targets for cancer therapy and inhibiting them may be particularly beneficial in Wnt-inactive HCCs.
Keywords: B9L; BCL9-2; Liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart BW, Wild CP. World Cancer Report 2014. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization. 2014
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

