The multifunctional peptide DN-9 produced peripherally acting antinociception in inflammatory and neuropathic pain via μ- and κ-opioid receptors
- PMID: 31444977
- PMCID: PMC6976790
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14848
The multifunctional peptide DN-9 produced peripherally acting antinociception in inflammatory and neuropathic pain via μ- and κ-opioid receptors
Abstract
Background and purpose: Considerable effort has recently been directed at developing multifunctional opioid drugs to minimize the unwanted side effects of opioid analgesics. We have developed a novel multifunctional opioid agonist, DN-9. Here, we studied the analgesic profiles and related side effects of peripheral DN-9 in various pain models.
Experimental approach: Antinociceptive effects of DN-9 were assessed in nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain. Whole-cell patch-clamp and calcium imaging assays were used to evaluate the inhibitory effects of DN-9 to calcium current and high-K+ -induced intracellular calcium ([Ca2+ ]i ) on dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons respectively. Side effects of DN-9 were evaluated in antinociceptive tolerance, abuse, gastrointestinal transit, and rotarod tests.
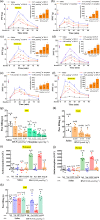
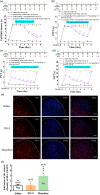
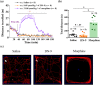
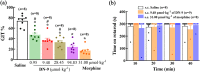
Key results: DN-9, given subcutaneously, dose-dependently produced antinociception via peripheral opioid receptors in different pain models without sex difference. In addition, DN-9 exhibited more potent ability than morphine to inhibit calcium current and high-K+ -induced [Ca2+ ]i in DRG neurons. Repeated treatment with DN-9 produced equivalent antinociception for 8 days in multiple pain models, and DN-9 also maintained potent analgesia in morphine-tolerant mice. Furthermore, chronic DN-9 administration had no apparent effect on the microglial activation of spinal cord. After subcutaneous injection, DN-9 exhibited less abuse potential than morphine, as was gastroparesis and effects on motor coordination.
Conclusions and implications: DN-9 produces potent analgesia with minimal side effects, which strengthen the candidacy of peripherally acting opioids with multifunctional agonistic properties to enter human studies to alleviate the current highly problematic misuse of classic opioids on a large scale.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Albert‐Vartanian, A. , Boyd, M. R. , Hall, A. L. , Morgado, S. J. , Nguyen, E. , Nguyen, V. P. , … Raffa, R. B. (2016). Will peripherally restricted κ‐opioid receptor agonists (pKORAs) relieve pain with less opioid adverse effects and abuse potential? Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 41, 371–382. 10.1111/jcpt.12404 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Roberts, R. E. , Broughton, B. R. S. , Sobey, C. G. , George, C. H. , Stanford, S. C. , … Ahluwalia, A. (2018). Goals and practicalities of immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry: A guide for submission to the British Journal of Pharmacology. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175, 407–411. 10.1111/bph.14112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al‐Khrasani, M. , Lackó, E. , Riba, P. , Király, K. , Sobor, M. , Timár, J. , … Fürst, S. (2012). The central versus peripheral antinociceptive effects of μ‐opioid receptor agonists in the new model of rat visceral pain. Brain Research Bulletin, 87, 238–243. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.10.018 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- lzujbky-2018-ot02/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities/International
- IRT_15R27/Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University/International
- 81673282/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81273355/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

