360-Degree Complex Primary Reconstruction Using Porous Tantalum Cages for Adult Degenerative Spinal Deformity
- PMID: 31448194
- PMCID: PMC6693065
- DOI: 10.1177/2192568218814531
360-Degree Complex Primary Reconstruction Using Porous Tantalum Cages for Adult Degenerative Spinal Deformity
Abstract
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Objective: To assess both implant performance and the amount of correction that can be achieved using multilevel anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF).
Methods: Retrospective cohort study (n = 178) performed over a 4-year period. Surgical variables examined included blood loss, operative time, perioperative complications, and secondary/revision procedures. Follow-up radiographic assessment was performed to record implant-related problems. Radiographic parameters were examined pre- and postoperatively. Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcome measures were collected preoperatively and at 6 weeks, 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years postoperatively. Descriptive and comparative statistical analysis, using paired-sample t test and repeated-measures analysis of variance (rANOVA), was performed.
Results: Lumbar lordosis increased from 42° ± 17° preoperatively to 55° ± 11° postoperatively (P < .001). The visual analog scale back pain mean score improved from 8.3 ± 1.5 preoperatively to 2.6 ± 2.4 at 2 years (P < .001). The mean Oswestry Disability Index improved from 69.5 ± 21.5 preoperatively to 19.9 ± 15.2 at 2 years (P < .001). The EQ-5D mean score improved from 0.2 ± 0.2 preoperatively to 0.8 ± 0.1 at 2 years (P = .02). There were no neurological, vascular, or visceral approach-related injuries reported. No rod breakages and no symptomatic nonunions occurred. There was one revision procedure performed for fracture.
Conclusions: The use of porous tantalum cages as part of a 360-degree fusion to treat adult degenerative spinal deformity has been demonstrated to be a safe and effective strategy, leading to good clinical, functional, and radiographic outcomes in the short term.
Keywords: ALIF; deformity; degenerative; interbody cage; lumbar; tantalum; trabecular metal.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


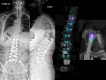
References
-
- Madigan L, Vaccaro AR, Spector LR, Milam RA. Management of symptomatic lumbar degenerative disc disease. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O’Shaughnessy BA. et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Phan K, Thayaparan GK, Mobbs RJ. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion—systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg. 2015;29:705–711. - PubMed
-
- Rao PJ, Loganathan A, Yeung V, Mobbs RJ. Outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery based on indication: a prospective study. Neurosurgery. 2015;76:7–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

