APOBEC3A Loop 1 Is a Determinant for Single-Stranded DNA Binding and Deamination
- PMID: 31448897
- PMCID: PMC7211764
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00394
APOBEC3A Loop 1 Is a Determinant for Single-Stranded DNA Binding and Deamination
Abstract
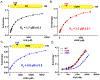
The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3 or A3) family of proteins functions in the innate immune system. The A3 proteins are interferon inducible and hypermutate deoxycytidine to deoxyuridine in foreign single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). However, this deaminase activity cannot discriminate between foreign and host ssDNA at the biochemical level, which presents a significant danger when A3 proteins gain access to the nucleus. Interestingly, this A3 capability can be harnessed when coupled with novel CRISPR-Cas9 proteins to create a targeted base editor. Specifically, A3A has been used in vitro to revert mutations associated with disease states. Recent structural studies have shown the importance of loop regions of A3A and A3G in ssDNA recognition and positioning for deamination. In this work, we further examined loop 1 of A3A to determine how it affects substrate selection, as well as the efficiency of deamination, in the hopes of advancing the potential of A3A in base editing technology. We found that mutating residue H29 enhanced deamination activity without changing substrate specificity. Also interestingly, we found that increasing the length of loop 1 decreases substrate specificity. Overall, these results lead to a better understanding of substrate recognition and deamination by A3A and the A3 family of proteins.
Figures
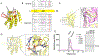

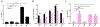

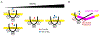
References
-
- Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Aparicio SA, Behjati S, Biankin AV, Bignell GR, Bolli N, Borg A, Borresen-Dale AL, Boyault S, Burkhardt B, Butler AP, Caldas C, Davies HR, Desmedt C, Eils R, Eyfjord JE, Foekens JA, Greaves M, Hosoda F, Hutter B, Ilicic T, Imbeaud S, Imielinski M, Jager N, Jones DT, Jones D, Knappskog S, Kool M, Lakhani SR, Lopez-Otin C, Martin S, Munshi NC, Nakamura H, Northcott PA, Pajic M, Papaemmanuil E, Paradiso A, Pearson JV, Puente XS, Raine K, Ramakrishna M, Richardson AL, Richter J, Rosenstiel P, Schlesner M, Schumacher TN, Span PN, Teague JW, Totoki Y, Tutt AN, Valdes-Mas R, van Buuren MM, van ‘t Veer L, Vincent-Salomon A, Waddell N, Yates LR, Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome, I., Consortium, I. B. C., Consortium, I. M.-S., PedBrain I, Zucman-Rossi J, Futreal PA, McDermott U, Lichter P., Meyerson M., Grimmond SM, Siebert R, Campo E, Shibata T, Pfister SM, Campbell PJ, and Stratton MR (2013) Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer, Nature 500, 415–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris RS, Petersen-Mahrt SK, and Neuberger MS (2002) RNA editing enzyme APOBEC1 and some of its homologs can act as DNA mutators, Mol Cell 10, 1247–1253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

