Sensors Driven AI-Based Agriculture Recommendation Model for Assessing Land Suitability
- PMID: 31450772
- PMCID: PMC6749515
- DOI: 10.3390/s19173667
Sensors Driven AI-Based Agriculture Recommendation Model for Assessing Land Suitability
Abstract
The world population is expected to grow by another two billion in 2050, according to the survey taken by the Food and Agriculture Organization, while the arable area is likely to grow only by 5%. Therefore, smart and efficient farming techniques are necessary to improve agriculture productivity. Agriculture land suitability assessment is one of the essential tools for agriculture development. Several new technologies and innovations are being implemented in agriculture as an alternative to collect and process farm information. The rapid development of wireless sensor networks has triggered the design of low-cost and small sensor devices with the Internet of Things (IoT) empowered as a feasible tool for automating and decision-making in the domain of agriculture. This research proposes an expert system by integrating sensor networks with Artificial Intelligence systems such as neural networks and Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) for the assessment of agriculture land suitability. This proposed system will help the farmers to assess the agriculture land for cultivation in terms of four decision classes, namely more suitable, suitable, moderately suitable, and unsuitable. This assessment is determined based on the input collected from the various sensor devices, which are used for training the system. The results obtained using MLP with four hidden layers is found to be effective for the multiclass classification system when compared to the other existing model. This trained model will be used for evaluating future assessments and classifying the land after every cultivation.
Keywords: IoT in agriculture; agricultural data; land suitability using sensors; multi-layer perceptron; sensor data in agriculture; smart agriculture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
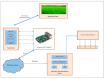
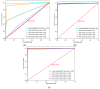
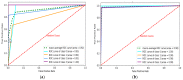

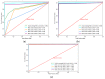
References
-
- Ahmed A.N., de Hussain I.D. Internet of Things (IoT) for smart precision agriculture and farming in rural areas. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018;5:4890–4899. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2879579. - DOI
-
- Elijah O., Rahman T.A., Orikumhi I., Leow C.Y., Hindia M.N. An overview of Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics in agriculture: benefits and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018;5:3758–3773. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2844296. - DOI
-
- Somov A., Shadrin D., Fastovets I., Nikitin A., Matveev S., Hrinchuk O. Pervasive Agriculture: IoT-Enabled Greenhouse for Plant Growth Control. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2018;17:65–75. doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2018.2873849. - DOI
-
- Bu F., Wang X. A smart agriculture IoT system based on deep reinforcement learning. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019;99:500–507. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.04.041. - DOI
-
- Alreshidi E. Smart Sustainable Agriculture (SSA) solution underpinned by Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) arXiv. 2019 doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2019.0100513.1906.03106 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

