Adipose Mesenchymal Extracellular Vesicles as Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Physiological Delivery Systems for Lung Regeneration
- PMID: 31450843
- PMCID: PMC6770759
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8090965
Adipose Mesenchymal Extracellular Vesicles as Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Physiological Delivery Systems for Lung Regeneration
Abstract
Accumulating evidence shows that Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSCs) exert their therapeutic effects by the release of secretome, made of both soluble proteins and nano/microstructured extracellular vesicles (EVs). In this work, for the first time, we proved by a proteomic investigation that adipose-derived (AD)-MSC-secretome contains alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), the main elastase inhibitor in the lung, 72 other proteins involved in protease/antiprotease balance, and 46 proteins involved in the response to bacteria. By secretome fractionation, we proved that AAT is present both in the soluble fraction of secretome and aggregated and/or adsorbed on the surface of EVs, that can act as natural carriers promoting AAT in vivo stability and activity. To modulate secretome composition, AD-MSCs were cultured in different stimulating conditions, such as serum starvation or chemicals (IL-1β and/or dexamethasone) and the expression of the gene encoding for AAT was increased. By testing in vitro the anti-elastase activity of MSC-secretome, a dose-dependent effect was observed; chemical stimulation of AD-MSCs did not increase their secretome anti-elastase activity. Finally, MSC-secretome showed anti-bacterial activity on Gram-negative bacteria, especially for Klebsiellapneumoniae. These preliminary results, in addition to the already demonstrated immunomodulation, pave the way for the use of MSC-secretome in the treatment of AAT-deficiency lung diseases.
Keywords: alpha-1-antitrypsin; anti-elastase; lung diseases; mesenchymal exosomes; mesenchymal extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal microvesicles; mesenchymal secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
M.L.T., S.P. and A.G.C. are members of the advisory board of the company PharmaExceed S.r.l.
Figures
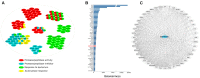
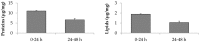
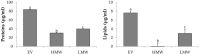
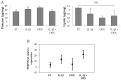


References
-
- De Girolamo L., Lucarelli E., Alessandri G., Avanzini M.A., Bernardo M.E., Biagi E., Brini A.T., D’Amico G., Fagioli F., Ferrero I., et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: A New “Cells as Drugs” Paradigm. Efficacy and Critical Aspects in Cell Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013;19:2459–2473. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319130015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crivelli B., Chlapanidas T., Perteghella S., Lucarelli E., Pascucci L., Brini A.T., Ferrero I., Marazzi M., Pessina A., Torre M.L. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell extracellular vesicles: From active principle to next generation drug delivery system. J. Control. Release. 2017;262:104–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

