Behavioral and Neural Pathways Supporting the Development of Prosocial and Risk-Taking Behavior Across Adolescence
- PMID: 31452199
- PMCID: PMC7317487
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13292
Behavioral and Neural Pathways Supporting the Development of Prosocial and Risk-Taking Behavior Across Adolescence
Abstract
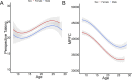
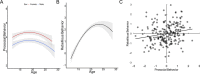
This study tested the pathways supporting adolescent development of prosocial and rebellious behavior. Self-report and structural brain development data were obtained in a three-wave, longitudinal neuroimaging study (8-29 years, N = 210 at Wave 3). First, prosocial and rebellious behavior assessed at Wave 3 were positively correlated. Perspective taking and intention to comfort uniquely predicted prosocial behavior, whereas fun seeking (current levels and longitudinal changes) predicted both prosocial and rebellious behaviors. These changes were accompanied by developmental declines in nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC) volumes, but only faster decline of MPFC (faster maturity) related to less rebellious behavior. These findings point toward a possible differential susceptibility marker, fun seeking, as a predictor of both prosocial and rebellious developmental outcomes.
© 2019 The Authors Child Development published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures
References
-
- Bault, N. , Joffily, M. , Rustichini, A. , & Coricelli, G. (2011). Medial prefrontal cortex and striatum mediate the influence of social comparison on the decision process. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, 16044–16049. 10.1073/pnas.1100892108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becht, A. I. , Bos, M. G. , Nelemans, S. A. , Peters, S. , Vollebergh, W. A. , Branje, S. J. , … Crone, E. A. (2018). Goal‐directed correlates and neurobiological underpinnings of adolescent identity: A multimethod multisample longitudinal approach. Child Development, 89, 823–836. 10.1111/cdev.13048 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blankenstein, N. E. , Schreuders, E. , Peper, J. S. , Crone, E. A. , & van Duijvenvoorde, A. C. K. (2018). Individual differences in risk‐taking tendencies modulate the neural processing of risky and ambiguous decision‐making in adolescence. NeuroImage, 172, 663–673. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.01.085 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

