The impact of belatacept on third-party HLA alloantibodies in highly sensitized kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 31452332
- PMCID: PMC6984982
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15585
The impact of belatacept on third-party HLA alloantibodies in highly sensitized kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
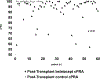
Recent evidence suggests that belatacept reduces the durability of preexisting antibodies to class I and class II human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). In this case series of 163 highly sensitized kidney transplant candidates whose calculated panel-reactive antibody (cPRA) activity was ≥98% to 100%, the impact of belatacept on preexisting HLA antibodies was assessed. Of the 163 candidates, 72 underwent transplantation between December 4, 2014 and April 15, 2017; 60 of these transplanted patients remained on belatacept consecutively for at least 6 months. We observed a decrease in the breadth and/or strength of HLA class I antibodies as assessed by FlowPRA in belatacept-treated patients compared to controls who did not receive belatacept. Specifically, significant HLA antibody reduction was evident for class I (P < .0009). Posttransplant belatacept-treated patients also had a clinically significant reduction in their cPRA compared to controls (P < .01). Collectively, these findings suggest belatacept can reduce HLA class I antibodies in a significant proportion of highly sensitized recipients and could be an option to improve pretransplant compatibility with organ donors.
Keywords: alloantibody; clinical research/practice; immunosuppressant - fusion proteins and monoclonal antibodies: belatacept; immunosuppression/immune modulation; kidney transplantation/nephrology; sensitization.
© 2019 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures
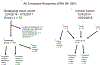



References
-
- Vieira CA, Agarwal A, Book BK, et al. Rituximab for reduction of anti-HLA antibodies in patients awaiting renal transplantation: 1. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics. Transplantation. 2004;77(4):542–548. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

