Long-term safety and efficacy of sarilumab plus methotrexate on disease activity, physical function and radiographic progression: 5 years of sarilumab plus methotrexate treatment
- PMID: 31452928
- PMCID: PMC6691511
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000887
Long-term safety and efficacy of sarilumab plus methotrexate on disease activity, physical function and radiographic progression: 5 years of sarilumab plus methotrexate treatment
Abstract
Objective: In MOBILITY (NCT01061736), sarilumab significantly reduced disease activity, improved physical function and inhibited radiographic progression at week 52 versus placebo in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and an inadequate response to methotrexate. We report 5-year safety, efficacy and radiographic outcomes of sarilumab from NCT01061736 and the open-label extension (EXTEND; NCT01146652), in which patients received sarilumab 200 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) + methotrexate.
Methods: Patients (n=1197) with moderately to severely active RA were initially randomised to placebo, sarilumab 150 mg or sarilumab 200 mg subcutaneously q2w plus weekly methotrexate for 52 weeks. Completers were eligible to enrol in the open-label extension and receive sarilumab 200 mg q2w + methotrexate.
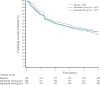
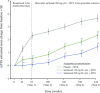
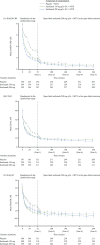
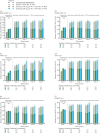
Results: Overall, 901 patients entered the open-label extension. The safety profile remained stable over 5-year follow-up and consistent with interleukin-6 receptor blockade. Absolute neutrophil count <1000 cells/mm3 was observed but not associated with increased infection rate. Initial treatment with sarilumab 200 mg + methotrexate was associated with reduced radiographic progression over 5 years versus sarilumab 150 mg + methotrexate or placebo + methotrexate (mean±SE change from baseline in van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score: 1.46±0.27, 2.35±0.28 and 3.68±0.27, respectively (p<0.001 for each sarilumab dose versus placebo)). Clinical efficacy was sustained through 5 years according to Disease Activity Score (28-joint count) using C reactive protein, Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index. The number of patients achieving CDAI ≤2.8 at 5 years was similar among initial randomisation groups (placebo, 76/398 (19%); sarilumab 150 mg, 68/400 (17%); sarilumab 200 mg, 84/399 (21%)).
Conclusion: Clinical efficacy, including inhibition of radiographic progression, reduction in disease activity and improvement in physical function, was sustained with sarilumab + methotrexate over 5 years. Safety appeared stable over the 5-year period.
Keywords: DMARDs (biological); rheumatoid arthritis; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MCG has received research grants or consulting fees from R-Pharm, Roche/Genentech and Sanofi Genzyme. DvdH has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Daiichi, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda and UCB. YL, SW and HvH are employees of Sanofi Genzyme and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. GSJ is an employee of Regeneron and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. JJG-R has received research support and/or consulting fees from Biogen, Gilead, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer and Roche. AK has received consulting fees and/or participated in speakers’ bureaus for AbbVie, Pfizer, Genentech, UCB, Sanofi/Regeneron, Celgene, Horizon and Merck. JAM-C has received consulting fees and/or participated in speakers’ bureaus for Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Sanofi Aventis, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Schering-Plough, Abbott, UCB, Eli Lilly and Gilead. MS has received consulting fees from R-Pharm. GRB has received research support and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB. BS has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Picerno V, Ferro F, Adinolfi A, et al. One year in review: the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015;33:551–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
