Engineered models to parse apart the metastatic cascade
- PMID: 31453371
- PMCID: PMC6704099
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-019-0092-3
Engineered models to parse apart the metastatic cascade
Abstract
While considerable progress has been made in studying genetic and cellular aspects of metastasis with in vitro cell culture and in vivo animal models, the driving mechanisms of each step of metastasis are still relatively unclear due to their complexity. Moreover, little progress has been made in understanding how cellular fitness in one step of the metastatic cascade correlates with ability to survive other subsequent steps. Engineered models incorporate tools such as tailored biomaterials and microfabrication to mimic human disease progression, which when coupled with advanced quantification methods permit comparisons to human patient samples and in vivo studies. Here, we review novel tools and techniques that have been recently developed to dissect key features of the metastatic cascade using primary patient samples and highly representative microenvironments for the purposes of advancing personalized medicine and precision oncology. Although improvements are needed to increase tractability and accessibility while faithfully simulating the in vivo microenvironment, these models are powerful experimental platforms for understanding cancer biology, furthering drug screening, and facilitating development of therapeutics.
Keywords: Cancer models; Metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


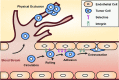

References
-
- Greshock Joel, Nathanson Katherine, Martin Anne-Marie, Zhang Lin, Coukos George, Weber Barbara L., Zaks Tal Z. Cancer Cell Lines as Genetic Models of Their Parent Histology: Analyses Based on Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization. Cancer Research. 2007;67(8):3594–3600. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3674. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Julien S., Merino-Trigo A., Lacroix L., Pocard M., Goere D., Mariani P., Landron S., Bigot L., Nemati F., Dartigues P., Weiswald L.-B., Lantuas D., Morgand L., Pham E., Gonin P., Dangles-Marie V., Job B., Dessen P., Bruno A., Pierre A., De The H., Soliman H., Nunes M., Lardier G., Calvet L., Demers B., Prevost G., Vrignaud P., Roman-Roman S., Duchamp O., Berthet C. Characterization of a Large Panel of Patient-Derived Tumor Xenografts Representing the Clinical Heterogeneity of Human Colorectal Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2012;18(19):5314–5328. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0372. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

