Identification of novel Glutathione S-Transferases epsilon 2 mutation in Anopheles maculipennis s.s. (Diptera: Culicidae)
- PMID: 31453404
- PMCID: PMC6702443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02262
Identification of novel Glutathione S-Transferases epsilon 2 mutation in Anopheles maculipennis s.s. (Diptera: Culicidae)
Abstract
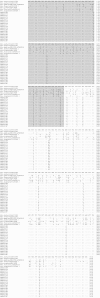
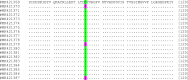
Anopheles maculipennis complex comprises some important malaria vectors in Iran, Middle East, and Europ. The principal way to control of malaria remains on the use of chemical insecticides against its vectors because there is no vaccine for malaria prevention. Extensive use of organophosphate compounds has caused to emergence and distribution of insecticide resistance in Anopheles species in Asia. The current study aimed to the detection of three well-known amino acid substitutions (I114T, L119F, and F120L) in the Glutathione S-Transferases epsilon 2 (GSTe2) gene are associated with DDT and organophosphate insecticides resistance in an Anopheles maculipennis population collected from Iran. Adult samples of An. maculipennis were collected by hand and Total catch in Animal and Human Shelters from Azerbaijan-Gharbi and Zanjan provinces. Following morphological identification, DNA was extracted by YTA Genomic DNA Extraction Mini Kit for amplification of rDNA-ITS2 and GSTe2 fragments. ∼500 bp fragment was amplified using F rDNA-ITS2 and GSTe2 primers. rDNA-ITS2 sequence analysis showed 100% similarity with An. maculipennis. GSTe2 nucleotide sequence similarity within species was 99-100%, while, it was 95-96 % when compared with Anopheles sacharovi GSTe2 sequences available in GenBank. Amino acid sequence comparisons showed a novel amino acid substitution in N148D position with 15.79% frequency. The current study reports new GSTe2 amino acid substitution in An. maculipennis s.s., for the first time. The function of the mutation N148D and its association with resistance phenotype need to validate. However, the integration of these data into the malaria control program still remains a challenge.
Keywords: Anopheles maculipennis; Bioinformatics; DNA sequencing; Genetics; Genomics; Glutathione S-Transferases epsilon 2; Molecular biology; Novel mutation; Polymorphism; Proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification, sequence analysis, and comparative study on GSTe2 insecticide resistance gene in three main world malaria vectors: Anopheles stephensi, Anopheles culicifacies, and Anopheles fluviatilis.J Med Entomol. 2006 Nov;43(6):1171-7. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585(2006)43[1171:isaacs]2.0.co;2. J Med Entomol. 2006. PMID: 17162949
-
The Anopheles maculipennis complex (Diptera: Culicidae) in Iran: molecular characterization and recognition of a new species.Bull Entomol Res. 2003 Dec;93(6):527-35. doi: 10.1079/ber2003272. Bull Entomol Res. 2003. PMID: 14704099
-
Molecular Characterization of Anopheles sacharovi Based on Sequences of ITS2-rDNA Region and COI Gene in North of Iran.J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019 Jun 24;13(2):135-144. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019. PMID: 31803774 Free PMC article.
-
The Anopheles maculipennis complex (Diptera: Culicidae) in Germany: an update following recent monitoring activities.Parasitol Res. 2016 Sep;115(9):3281-94. doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5189-9. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 27444437 Review.
-
Insecticide resistance in Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae) could compromise the sustainability of malaria vector control strategies in West Africa.Acta Trop. 2013 Oct;128(1):7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23792227 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring of synthetic insecticides resistance and mechanisms among malaria vector mosquitoes in Iran: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2022 Jan 24;8(1):e08830. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08830. eCollection 2022 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35128113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autogeny in Culiseta longiareolata (Culicidae: Diptera) mosquitoes in laboratory conditions in Iran.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Feb 19;13(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-04942-5. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32075679 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially-explicit genomics of An. gambiae s.l uncovers fine-scale population structure and mechanisms of insecticide resistance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 23:2025.06.13.655782. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.13.655782. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667006 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Akiner M., Caglar S., Simsek F. Yearly changes of insecticide susceptiblity and possible insecticide resistance mechanisms of Anopheles maculipennis Meigen (Diptera: Culicidae) in Turkey. Acta Trop. 2013;126:280–285. - PubMed
-
- Azari-Hamidian S. Checklist of Iranian mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) J. Vector Ecol. 2007;32:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Azari-Hamidian S., Harbach R.E. Keys to the adult females and fourth-instar larvae of the mosquitoes of Iran (Diptera: Culicidae) Zootaxa. 2009;2078:1–33.
-
- Azari-Hamidian S., Norouzi B., Harbach R.E. A detailed review of the mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) of Iran and their medical and veterinary importance. Acta Trop. 2019;194:106–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

