Interactive influence of rainfall manipulation and livestock grazing on species diversity of the herbaceous layer community in a humid savannah in Kenya
- PMID: 31453419
- PMCID: PMC6702439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pld.2019.04.005
Interactive influence of rainfall manipulation and livestock grazing on species diversity of the herbaceous layer community in a humid savannah in Kenya
Abstract
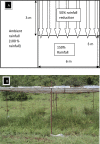
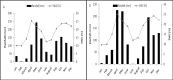
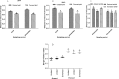
Changes in rainfall regime and grazing pressure affect vegetation composition and diversity with ecological implications for savannahs. The savannah in East Africa has experienced increased livestock grazing and rainfall variability but the impacts associated with those changes on the herbaceous layer have rarely been documented. We investigated the effect of livestock grazing, rainfall manipulation and their interaction on the composition and diversity of the herbaceous community in the savannah for two years in Lambwe, Kenya. Rainfall manipulation plots were set up for vegetation sampling; these plots received either 50% more or 50% less rainfall than control plots. Simpson's diversity and Berger-Parker indices were used to determine diversity changes and dominance respectively. The frequency of species was used to compute their abundance and their life forms as determined from the literature. Grazing significantly increased species diversity through suppression of dominant species. Rainfall manipulation had no significant impact on plant diversity in fenced plots, but rainfall reduction significantly reduced diversity in grazed plots. In contrast, rainfall manipulation had no impact on dominance in either fenced or grazed plots. The interaction of grazing and rainfall manipulation is complex and will require additional survey campaigns to create a complete picture of the implications for savannah structure and composition.
Keywords: Grazing; Moist savannah; Plant diversity; Rainfall.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of livestock grazing and rainfall manipulation enhances herbaceous species diversity and aboveground biomass in a humid savanna.J Plant Res. 2019 May;132(3):345-358. doi: 10.1007/s10265-019-01105-x. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Plant Res. 2019. PMID: 30980217
-
Herbivory and drought generate short-term stochasticity and long-term stability in a savanna understory community.Ecol Appl. 2018 Mar;28(2):323-335. doi: 10.1002/eap.1649. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Ecol Appl. 2018. PMID: 29140577
-
Measuring plant diversity in the tall threetip sagebrush steppe: influence of previous grazing management practices.Environ Manage. 2003 Aug;32(2):234-45. doi: 10.1007/s00267-003-0073-7. Environ Manage. 2003. PMID: 14753648
-
The impact of livestock grazing on plant diversity: an analysis across dryland ecosystems and scales in southern Africa.Ecol Appl. 2014 Jul;24(5):1188-203. doi: 10.1890/13-0377.1. Ecol Appl. 2014. PMID: 25154106
-
Low carbon and environmentally friendly livestock. The Costa Rican approach.Anim Front. 2021 Sep 6;11(4):44-46. doi: 10.1093/af/vfab036. eCollection 2021 Jul. Anim Front. 2021. PMID: 34513268 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Water Buffalo's Adaptability to Different Environments and Farming Systems: A Review.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 24;15(11):1538. doi: 10.3390/ani15111538. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40509004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ecological Drivers of Community Cohesion.mSystems. 2023 Feb 23;8(1):e0092922. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00929-22. Epub 2023 Jan 19. mSystems. 2023. PMID: 36656037 Free PMC article.
-
Building a better plant world through mutual learning: An introduction to a special issue on plant diversity and conservation in the Belt & Road Countries.Plant Divers. 2019 Jun 28;41(3):133-134. doi: 10.1016/j.pld.2019.06.008. eCollection 2019 Jun. Plant Divers. 2019. PMID: 31453413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abrams A. Monotonic or unimodal diversity-productivity gradient: What does competition theory predict? Ecology. 1995;76(7):2019–2027.
-
- Arnhold S., Otieno D., Onyango J., Koeller T., Huwe B., Tenhunen J. Soil properties along a gradient from hillslopes to the savanna plains in the Lambwe Valley, Kenya. Soil Tillage Res. 2015;154:75–83.
-
- Augustine J. Spatial heterogeneity of herbaceous layer of a semi-arid savannah ecosystem. Plant Ecol. 2003;167:319–332.
-
- Bakker C., Blair J., Knnap A. Does resource availability, resource heterogeneity or species turnover mediate changes in plant species richness in grazed grassland? Oecologia. 2003;137:385–391. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

