Maladaptive Aggression: With a Focus on Impulsive Aggression in Children and Adolescents
- PMID: 31453715
- PMCID: PMC6786344
- DOI: 10.1089/cap.2019.0039
Maladaptive Aggression: With a Focus on Impulsive Aggression in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
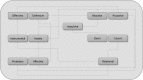
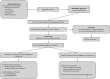
Objective: Aggressive behavior is among the most common reasons for referral to psychiatric clinics and confers significant burden on individuals. Aggression remains poorly defined; there is currently no consensus on the best ways to recognize, diagnose, and treat aggression in clinical settings. In this review, we synthesize the available literature on aggression in children and adolescents and propose the concept of impulsive aggression (IA) as an important construct associated with diverse and enduring psychopathology. Methods: Articles were identified and screened from online repositories, including PubMed, PsychInfo, the Cochrane Database, EMBase, and relevant book chapters, using combinations of search terms such as "aggression," "aggressive behavio(u)r," "maladaptive aggression," "juvenile," and "developmental trajectory." These were evaluated for quality of research before being incorporated into the article. The final report references 142 sources, published from 1987 to 2019. Results: Aggression can be either adaptive or maladaptive in nature, and the latter may require psychosocial and biomedical interventions when it occurs in the context of central nervous system psychopathology. Aggression can be categorized into various subtypes, including reactive/proactive, overt/covert, relational, and IA. IA in psychiatric or neurological disorders is reviewed along with current treatments, and an algorithm for systematic evaluation of aggression in the clinical setting is proposed. Conclusions: IA is a treatable form of maladaptive aggression that is distinct from other aggression subtypes. It occurs across diverse psychiatric and neurological diagnoses and affects a substantial subpopulation. IA can serve as an important construct in clinical practice and has considerable potential to advance research.
Keywords: aggression; impulsive aggression; maladaptive aggression; neurological disorders; psychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
D.F. Connor reports the following: Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (consultant) and Shire Pharmaceuticals (grant).
J.H. Newcorn reports the following: Akili Interactive (consultant); Alcobra (consultant); Arbor (consultant); Cingulate Therapeutics (consultant); Enzymotec (consultant and research support); KemPharm (consultant); Lundbeck (consultant and research support); Medice (consultant); NLS Pharma (consultant); Pfizer (consultant); Rhodes (consultant); Shire (consultant and research support); Sunovion (consultant); and Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (consultant).
K.E. Saylor reports the following: Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (consultant); Neurovance (consultant); Alcobra (consultant); Eli Lilly (consultant); Otsuka (consultant); Purdue (consultant); and Shire Pharmaceuticals (consultant).
B.H. Amann reports the following: Ironshore Pharmaceuticals & Development, Inc., Purdue Pharma L.P., Akili Interactive, Tris Pharma, Inc., Rhodes Pharmaceuticals L.P., Neos Therapeutics, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Lundbeck, Inc., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Shire Plc, and Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
L. Scahill reports the following: American Psychological Association (royalties); Department of Defense (research support); Guilford Press (royalties); Janssen (consultant); National Institutes of Health (research support); Neurocrine (consultant); Oxford Press (royalties); Roche (consultant); Shire (consultant); Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (consultant); Teva (consultant); and Yamo (consultant).
A.S. Robb reports the following: Actavis/Forest Laboratories (consultant, research support, and travel support); Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. (data safety monitoring board); AACAP (honorarium and travel support); AAP (honorarium, travel support); Bracket (consultant); Case Western Reserve (honorarium and travel support); Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Society of Greater Washington (honorarium); College of Neurologic and Psychiatric Pharmacists (honorarium and travel support); Eli Lilly (royalties); GlaxoSmithKline (royalties); Guilford Press (royalties); Johnson & Johnson (royalties); Lundbeck/Takeda (advisor, research support, and travel support); Neuronetics (data safety monitoring board); Neuroscience Education Institute (honorarium and travel support); Nevada Psychiatric Association (honorarium and travel support); National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (research support); NICHD (advisor); NIMH (data safety monitoring board); NINDS (research support); NACCME (honorarium and travel support); Pfizer, Inc. (research support, stock/equity, and travel support); Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (advisor and travel support); Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (research support); SyneuRx (research support); and University of Cambridge (advisor).
P.S. Jensen reports the following: REACH Institute (board member, travel support); Guilford Press (royalties); APPI (royalties); Random House (royalties); Oxford Press (royalties); CATCH Services, LLC (shareholder); Ironshore Pharmaceuticals & Development, Inc. (consultant); and Shire Pharmaceuticals (consultant and grant).
B. Vitiello reports the following: Medice (consultant) and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries (consultant).
R.L. Findling reports the following: Aevi Genomic Medicine (research support and consultant); Akili (research support, consultant); Alcobra Pharma (research support and consultant); AACAP (speaker's bureau); Amarex Clinical Research (consultant); American Psychiatric Press (royalties); Bracket (consultant); ePharmaSolutions (consultant); Forest Laboratories, Inc. (research support); Genentech (consultant); Guilford Press (consultant); Ironshore Pharmaceuticals & Development, Inc. (consultant); KemPharm, Inc. (consultant); Lundbeck, Inc. (research support and consultant); Merck & Co., Inc. (consultant); National Institutes of Health (research support and consultant); Neurim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (research support and consultant); Nuvelution Pharmaceuticals (consultant); Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. (consultant); PCORI (research support); Pfizer, Inc. (research support); Physicians Postgraduate Press (consultant); Purdue Pharma L.P. (research support); Roche (research support); Sage Therapeutics (royalties); Shire (research support); Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (research support, consultant); Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (research support and consultant); SyneuRx (research support); Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (consultant); TouchPoint (consultant); Tris Pharma, Inc. (consultant); and Validus Pharmaceuticals LLC (research support and consultant).
J.K. Buitelaar reports the following: Janssen Cilag BV (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Eli Lilly (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Lundbeck (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Shire (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Roche (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Medice (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Novartis (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Servier (consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker); Roche (research support); and Vifor (research support).
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013
-
- Archer J. and Coyne SM: An integrated review of indirect, relational, and social aggression. Pers Soc Psychol Rev 9:212–230, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bambauer KZ, Connor DF: Characteristics of aggression in clinically referred children. CNS Spectr 10:709–718, 2005 - PubMed

