Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®): Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 31454891
- PMCID: PMC6784247
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11090489
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®): Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
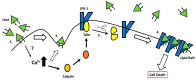
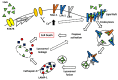
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is an oral pathogen that produces the RTX toxin, leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®). A. actinomycetemcomitans is strongly associated with the development of localized aggressive periodontitis. LtxA acts as a virulence factor for A. actinomycetemcomitans to subvert the host immune response by binding to the β2 integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1; CD11a/CD18) on white blood cells (WBCs), causing cell death. In this paper, we reviewed the state of knowledge on LtxA interaction with WBCs and the subsequent mechanisms of induced cell death. Finally, we touched on the potential therapeutic applications of LtxA (trade name Leukothera®) toxin therapy for the treatment of hematological malignancies and immune-mediated diseases.
Keywords: Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans; RTX (repeats-in-toxin) toxin; cell death; leukotoxin (LtxA); lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1); oral microbiology; toxin therapy; virulence factor; β2 integrins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. Scott C. Kachlany owns stock in the company (Actinobac Biomed, Inc.) that has licensed the clinical use of leukotoxin. Benjamin A. Belinka Jr. is an employee of Actinobac Biomed, Inc., and owns stock in this company. In addition, Scott C. Kachlany and Brian A. Vega have received consulting fees from Actinobac Biomed, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Shenker B.J., McKay T., Datar S., Miller M., Chowhan R., Demuth D. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans immunosuppressive protein is a member of the family of cytolethal distending toxins capable of causing a G2 arrest in human T cells. J. Immunol. (Baltim. Md. 1950) 1999;162:4773–4780. - PubMed
-
- Shenker B.J., Besack D., McKay T., Pankoski L., Zekavat A., Demuth D.R. Induction of cell cycle arrest in lymphocytes by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans cytolethal distending toxin requires three subunits for maximum activity. J. Immunol. 2005;174:2228–2234. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2228. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

