Characterization of Polysulfides, Polysulfanes, and Other Unique Species in the Reaction between GSNO and H2S
- PMID: 31454893
- PMCID: PMC6749520
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24173090
Characterization of Polysulfides, Polysulfanes, and Other Unique Species in the Reaction between GSNO and H2S
Erratum in
-
Correction: Kumar, M.R., et al. Characterization of Polysulfides, Polysulfanes, and Other Unique Species in the Reaction between GSNO and H2S. Molecules 2019, 24, 3090.Molecules. 2019 Dec 16;24(24):4610. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244610. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31888298 Free PMC article.
Abstract
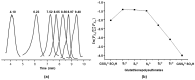
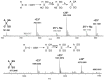
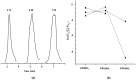
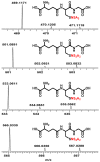
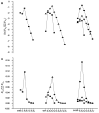
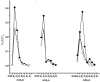
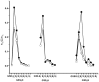
Glutathione-based products, GSnX, of the reaction of hydrogen sulfide, H2S, S-nitroso glutathione, and GSNO, at varied stoichiometries have been analyzed by liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) and chemical trapping experiments. A wide variety of glutathione-based species with catenated sulfur chains have been identified including sulfanes (GSSnG), sulfides (GSSnH), and sulfenic acids (GSnOH); sulfinic (GSnO2H) and sulfonic (GSnO3H) acids are also seen in reactions exposed to air. The presence of each species of GSnX within the original reaction mixtures was confirmed using Single Ion Chromatograms (SICs), to demonstrate the separation on the LC column, and given approximate quantification by the peak area of the SIC. Further, confirmation for different GSnX families was obtained by trapping with species-specific reagents. Several unique GSnX families have been characterized, including bridging mixed di- and tetra-valent polysulfanes and internal trithionitrates (GSNHSnH) with polysulfane branches. Competitive trapping experiments suggest that the polysulfane chains are formed via the intermediacy of sulfenic acid species, GSSnOH. In the presence of radical trap vinylcyclopropane (VCP) the relative distributions of polysulfane speciation are relatively unaffected, suggesting that radical coupling is not a dominant pathway. Therefore, we suggest polysulfane catenation occurs via reaction of sulfides with sulfenic acids.
Keywords: S-nitroso glutathione; dimedone; high-resolution mass spectrometry; hydrogen sulfide; iodoacetamide; polysulfanes; sulfenic acids; sulfides; vinylcyclopropane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
S-Transnitrosation reactions of hydrogen sulfide (H2S/HS-/S2-) with S-nitrosated cysteinyl thiols in phosphate buffer of pH 7.4: Results and review of the literature.Nitric Oxide. 2017 May 1;65:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Nitric Oxide. 2017. PMID: 28185882
-
Chemical trapping and characterization of small oxoacids of sulfur (SOS) generated in aqueous oxidations of H2S.Redox Biol. 2018 Apr;14:485-491. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.012. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29096321 Free PMC article.
-
Reaction of Hydrogen Sulfide with Disulfide and Sulfenic Acid to Form the Strongly Nucleophilic Persulfide.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 6;290(45):26866-26880. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.672816. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26269587 Free PMC article.
-
Biological chemistry of hydrogen sulfide and persulfides.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Mar 1;617:9-25. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.09.018. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 27697462 Review.
-
Reactivity of Small Oxoacids of Sulfur.Molecules. 2019 Jul 30;24(15):2768. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152768. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31366103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species (RONSS) as a Metabolic Cluster for Signaling and Biostimulation of Plants: An Overview.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;11(23):3203. doi: 10.3390/plants11233203. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction: Kumar, M.R., et al. Characterization of Polysulfides, Polysulfanes, and Other Unique Species in the Reaction between GSNO and H2S. Molecules 2019, 24, 3090.Molecules. 2019 Dec 16;24(24):4610. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244610. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31888298 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Reactive Sulfur Metabolome: Intracellular and Efflux Measurements of Small Oxoacids of Sulfur (SOS) and H2S in Human Primary Vascular Cell Culture.Molecules. 2021 Nov 26;26(23):7160. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237160. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885743 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Endogenous and Extruded H2S and Small Oxoacids of Sulfur (SOS) in Cell Cultures.ACS Chem Biol. 2021 Aug 20;16(8):1413-1424. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00257. Epub 2021 Aug 10. ACS Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34374506 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology-based investigation of brugine reveals its multi-target molecular mechanism against Breast Cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jun 12;40(7):202. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02067-w. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37308611
References
-
- Fukuto J.M., Carrington S.J., Tantillo D.J., Harrison J.G., Ignarro L.J., Freeman B.A., Chen A., Wink D.A. Small Molecule Signaling Agents: The Integrated Chemistry and Biochemistry of Nitrogen Oxides, Oxides of Carbon, Dioxygen, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Their Derived Species. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012;25:769–793. doi: 10.1021/tx2005234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

