Structural basis of Q-dependent antitermination
- PMID: 31455742
- PMCID: PMC6744881
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1909801116
Structural basis of Q-dependent antitermination
Abstract
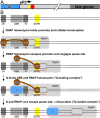
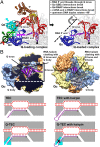
Lambdoid bacteriophage Q protein mediates the switch from middle to late bacteriophage gene expression by enabling RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through transcription terminators preceding bacteriophage late genes. Q loads onto RNAP engaged in promoter-proximal pausing at a Q binding element (QBE) and adjacent sigma-dependent pause element (SDPE) to yield a Q-loading complex, and Q subsequently translocates with RNAP as a pausing-deficient, termination-deficient Q-loaded complex. Here, we report high-resolution structures of 4 states on the pathway of antitermination by Q from bacteriophage 21 (Q21): Q21, the Q21-QBE complex, the Q21-loading complex, and the Q21-loaded complex. The results show that Q21 forms a torus, a "nozzle," that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, extruding topologically linked single-stranded RNA and preventing the formation of pause and terminator hairpins.
Keywords: RNA polymerase; transcription antitermination; transcription antitermination factor Q; transcription antitermination factor Q21; transcription elongation complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Grayhack E. J., Roberts J. W., The phage lambda Q gene product: Activity of a transcription antiterminator in vitro. Cell 30, 637–648 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Grayhack E. J., Yang X. J., Lau L. F., Roberts J. W., Phage lambda gene Q antiterminator recognizes RNA polymerase near the promoter and accelerates it through a pause site. Cell 42, 259–269 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Yarnell W. S., Roberts J. W., The phage lambda gene Q transcription antiterminator binds DNA in the late gene promoter as it modifies RNA polymerase. Cell 69, 1181–1189 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Ring B. Z., Roberts J. W., Function of a nontranscribed DNA strand site in transcription elongation. Cell 78, 317–324 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

