Refinement of risk stratification for childhood rhabdomyosarcoma using FOXO1 fusion status in addition to established clinical outcome predictors: A report from the Children's Oncology Group
- PMID: 31456361
- PMCID: PMC6797586
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2504
Refinement of risk stratification for childhood rhabdomyosarcoma using FOXO1 fusion status in addition to established clinical outcome predictors: A report from the Children's Oncology Group
Abstract
Background: Previous studies of the prognostic importance of FOXO1 fusion status in patients with rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) have had conflicting results. We re-examined risk stratification by adding FOXO1 status to traditional clinical prognostic factors in children with localized or metastatic RMS.
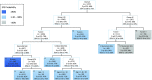
Methods: Data from six COG clinical trials (D9602, D9802, D9803, ARST0331, ARTS0431, ARST0531; two studies each for low-, intermediate- and high-risk patients) accruing previously untreated patients with RMS from 1997 to 2013 yielded 1727 evaluable patients. Survival tree regression for event-free survival (EFS) was conducted to recursively select prognostic factors for branching and split. Factors included were age, FOXO1, clinical group, histology, nodal status, number of metastatic sites, primary site, sex, tumor size, and presence of metastases in bone/bone marrow, soft tissue, effusions, lung, distant lymph nodes, and other sites. Definition and outcome of the proposed risk groups were compared to existing systems and cross-validated results.
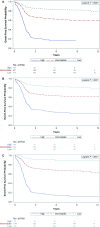
Results: The 5-year EFS and overall survival (OS) for evaluable patients were 69% and 79%, respectively. Extent of disease (localized versus metastatic) was the first split (EFS 73% vs 30%; OS 84% vs. 42%). FOXO1 status (positive vs negative) was significant in the second split both for localized (EFS 52% vs 78%; OS 65% vs 88%) and metastatic disease (EFS 6% vs 46%; OS 19% vs 58%).
Conclusions: After metastatic status, FOXO1 status is the most important prognostic factor in patients with RMS and improves risk stratification of patients with localized RMS. Our findings support incorporation of FOXO1 status in risk stratified clinical trials.
Keywords: fusion status; rhabdomyosarcoma; risk stratification; survival tree regression.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None: Dasgupta, Chi, Meyer, Rudzinski, Hibbitts, Rodeberg, Skapek, Spunt. Positive disclosures: Arndt ‐‐ stock ownership Pfizer and Merck; Bradley‐‐ honoraria and travel funding from Ion Beam applications; Hawkins‐‐ travel funding from Bayer, BMS, loxo oncology, Celgene; Barr‐‐ stock ownership by self or immediate family member in Abbott Labs, General Electric, Danaher corp, Abbvie inc, Baxter international, Celgene, Colgate Palmolive, Edwards lifesciences, Eli Lilly, Johnson and Johnson; Wolden—travel expenses from IBA and consulting role in Y‐mAbs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous