Computationally Designed 1,2,4-Triazolylidene-Derived N-Heterocyclic Olefins for CO2 Capture, Activation, and Storage
- PMID: 31457230
- PMCID: PMC6641026
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00411
Computationally Designed 1,2,4-Triazolylidene-Derived N-Heterocyclic Olefins for CO2 Capture, Activation, and Storage
Abstract
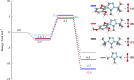
In this article, triazolylidene-derived N-heterocyclic olefins (trNHOs) are designed using computational quantum tools, and their potential to promote CO2 sequestration is tested and discussed in detail. The low barrier heights related to the trNHO-mediated process indicate that the tailored compounds are very promising for fast CO2 sequestration. The systematic analysis of the presence of distinct substitutes at different N positions of the trNHO ring allows us to rationalize their effect on the carboxylation process and reveal the best N-substituted trNHO systems for CO2 sequestration and improved trNHO carboxylates for faster CO2 capture/release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






References
-
- Fiorani G.; Guo W.; Kleij A. W. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1375–1389. 10.1039/C4GC01959H. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

