Dissolved Selenium(VI) Removal by Zero-Valent Iron under Oxic Conditions: Influence of Sulfate and Nitrate
- PMID: 31457519
- PMCID: PMC6640955
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00382
Dissolved Selenium(VI) Removal by Zero-Valent Iron under Oxic Conditions: Influence of Sulfate and Nitrate
Abstract
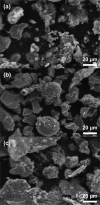
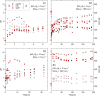
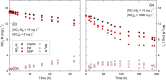
Dissolved Se(VI) removal by three commercially available zero-valent irons (ZVIs) was examined in oxic batch experiments under circumneutral pH conditions in the presence and absence of NO3 - and SO4 2-. Environmentally relevant Se(VI) (1 mg L-1), NO3 - ([NO3-N] = 15 mg L-1), and SO4 2- (1800 mg L-1) were employed to simulate mining-impacted waters. Ninety percent of Se(VI) removal was achieved within 4-8 h in the absence of SO4 2- and NO3 -. A similar Se(VI) removal rate was observed after 10-32 h in the presence of NO3 -. Dissolved Se(VI) removal rates exhibited the highest decrease in the presence of SO4 2-; 90% of Se(VI) removal was measured after 50-191 h for SO4 2- and after 150-194 h for SO4 2- plus NO3 - depending on the ZVI tested. Despite differences in removal rates among batches and ZVI materials, Se(VI) removal consistently followed first-order reaction kinetics. Scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses of reacted solids showed that Fe(0) present in ZVI undergoes oxidation to magnetite [Fe3O4], wüstite [FeO], lepidocrocite [γ-FeOOH], and goethite [α-FeOOH] over time. X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy indicated that Se(VI) was reduced to Se(IV) and Se(0) during removal. These results demonstrate that ZVI can be effectively used to control Se(VI) concentrations in mining-impacted waters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selenate removal by zero-valent iron in oxic condition: the role of Fe(II) and selenate removal mechanism.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jan;23(2):1081-90. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4578-4. Epub 2015 May 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 25943509
-
Zero-valent iron for the abatement of arsenate and selenate from flowback water of hydraulic fracturing.Chemosphere. 2017 Jan;167:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.120. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Chemosphere. 2017. PMID: 27718428
-
Enhanced removal of Se(VI) from water via pre-corrosion of zero-valent iron using H2O2/HCl: Effect of solution chemistry and mechanism investigation.Water Res. 2018 Apr 15;133:173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.038. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Water Res. 2018. PMID: 29407699
-
Kinetics and mechanisms of pH-dependent selenite removal by zero valent iron.Water Res. 2013 Oct 1;47(15):5846-55. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.011. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Water Res. 2013. PMID: 23899877
-
Enhanced removal of selenate from mining effluent by H2O2/HCl-pretreated zero-valent iron.Water Sci Technol. 2018 Dec;78(11):2404-2413. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.526. Water Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 30699092
Cited by
-
Influences of pH on transport of arsenate (As5+) through different reactive media using column experiments and transport modeling.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 26;10(1):3512. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59770-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32103033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griffith M. B.; Norton S. B.; Alexander L. C.; Pollard A. I.; LeDuc S. D. The effects of mountaintop mines and valley fills on the physicochemical quality of stream ecosystems in the central Appalachians: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 1–12. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.12.042. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

