Two Highly Stable Luminescent Lead Phosphonates Based on Mixed Ligands: Highly Selective and Sensitive Sensing for Thymine Molecule and VO3 - Anion
- PMID: 31458280
- PMCID: PMC6643760
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02030
Two Highly Stable Luminescent Lead Phosphonates Based on Mixed Ligands: Highly Selective and Sensitive Sensing for Thymine Molecule and VO3 - Anion
Abstract
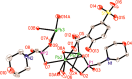
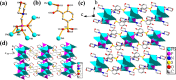
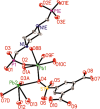
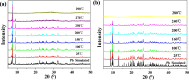
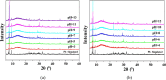
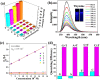
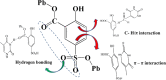
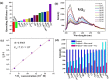
Two luminescent lead phosphonates with two-dimensional (2D) layer and three-dimensional (3D) framework structure, namely, Pb3[(L1)2(Hssc)(H2O)2] (1) and [Pb2(L2)0.5(bts)(H2O)2]·H2O (2) (H2L1 = O(CH2CH2)2NCH2PO3H2, H4L2 = H2PO3CH2NH(C2H4)2NHCH2PO3H2, H3ssc = 5-sulfosalicylic acid, NaH2bts = 5-sulfoisophthalic acid sodium) have been prepared via hydrothermal techniques. The two compounds not only show excellent thermal stability but also remain intact in aqueous solution within an extensive pH range. Moreover, the atomic absorption spectroscopy analysis experiment indicates that there does not exist the leaching of Pb2+ ions from the lead phosphonates, which show they are nontoxic in aqueous solution. In compound 1, the Pb(1)O4, Pb(2)O7, Pb(3)O4, and CPO3 polyhedra are interlinked into a one-dimensional chain, which is further connected to adjacent chain by sharing the Hssc2- to form a 2D layer. Interestingly, compound 1 as a highly selective and sensitive luminescent material can be used to detect the thymine molecule with a very low detection limit of 8.26 × 10-7 M. In compound 2, the Pb(1)O6 and Pb(2)O5 polyhedra are interlinked into a dimer via edge sharing, which is further connected to adjacent dimer to form a tetramer via corner sharing, and such a tetramer is then interlinked into a 2D layer through bts3- ligands; the adjacent 2D layers are finally constructed to a 3D structure by sharing the L2 4- ligand. Compound 2 can be applied as an excellent luminescent sensor for sensing of VO3 - anion. Furthermore, the probable fluorescent quenching mechanisms of the two compounds have also been studied.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bazzicalupi C.; Bencini A.; Berni E.; Bianchi A.; Ciattini S.; Giorgi C.; Paoletti P.; Valtancoli B. Supramolecular assembling of dizinc macrocyclic complexes with thymine and uracil-the role of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 3, 629–632. 10.1002/1099-0682(200103)2001:33.0.CO;2-N. - DOI
-
- Li L.; Bian R. X.; Ding Y. P.; Yu M. L.; Yu D. W. Application of functionalized ZnS nanoparticles to determinate uracil and thymine as a fluorescence probe. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 905–908. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.08.050. - DOI
-
- Luvino D.; Gasparutto D.; Reynaud S.; Smietana M.; Vasseur J. J. Boronic acid-based fluorescent receptors for selective recognition of thymine glycol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6075–6078. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.07.173. - DOI
-
- Liu C. X.; Chen Y. Q.; Wang Y. F.; Wu F.; Zhang X.; Yang W.; Wang J. Q.; Chen Y.; He Z. Y.; Zou G. R.; Wang S. R.; Zhou X. A highly efficient fluorescence-based switch-on detection method of 5-formyluracil in DNA. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2449–2458. 10.1007/s12274-017-1445-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

