Biobased Acrylate Photocurable Resin Formulation for Stereolithography 3D Printing
- PMID: 31458469
- PMCID: PMC6641428
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01648
Biobased Acrylate Photocurable Resin Formulation for Stereolithography 3D Printing
Abstract
To facilitate the ongoing transition toward a circular economy, the availability of renewable materials for additive manufacturing becomes increasingly important. Here, we report the successful fabrication of complex shaped prototypes from biobased acrylate photopolymer resins, employing a commercial stereolithography apparatus (SLA) 3D printer. Four distinct resins with a biobased content ranging from 34 to 67% have been developed. All formulations demonstrated adequate viscosity and were readily polymerizable by the UV-laser-based SLA process. Increasing the double-bond concentration within the resin results in stiff and thermally resilient 3D printed products. High-viscosity resins lead to high-resolution prototypes with a complex microarchitecture and excellent surface finishing, comparable to commercial nonrenewable resins. These advances can facilitate the wide application of biobased resins for construction of new sustainable products via stereolithographic 3D printing methods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
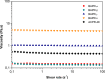
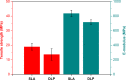

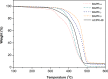
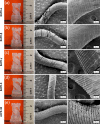
References
-
- van Wijk A.; van Wijk I.. 3D Printing with Biomaterials: Towards a Sustainable and Circular Economy; IOS Press: Amsterdam, 2015.
-
- Bhatia S. K.; Ramadurai K. W.. 3D Printing and Bio-Based Materials in Global Health; Springer: Cham, 2017.
-
- Kreiger M.; Pearce J. M. Environmental Life Cycle Analysis of Distributed Three-Dimensional Printing and Conventional Manufacturing of Polymer Products. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1511–1519. 10.1021/sc400093k. - DOI
-
- Hull C. W.Apparatus for production of three-dimensional objects by stereolithography. U.S. Patent 4,575,330, 1986.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

