Direct Z-Scheme Cs2O-Bi2O3-ZnO Heterostructures as Efficient Sunlight-Driven Photocatalysts
- PMID: 31459301
- PMCID: PMC6645477
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01449
Direct Z-Scheme Cs2O-Bi2O3-ZnO Heterostructures as Efficient Sunlight-Driven Photocatalysts
Abstract
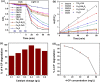
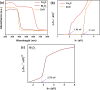
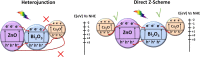
Limited light absorption, inefficient electron-hole separation, and unsuitable positions of conduction band bottom and/or valence band top are three major critical issues associated with high-efficiency photocatalytic water treatment. An attempt has been carried out here to address these issues through the synthesis of direct Z-scheme Cs2O-Bi2O3-ZnO heterostructures via a facile, fast, and economic method: solution combustions synthesis. The photocatalytic performances are examined by the 4-chlorophenol degradation test under simulated sunlight irradiation. UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy analysis, electrochemical impedance test, and the observed transient photocurrent responses prove not only the significant role of Cs2O in extending light absorption to visible and near-infrared regions but also its involvement in charge carrier separation. Radical-trapping experiments verify the direct Z-scheme approach followed by the charge carriers in heterostructured Cs2O-Bi2O3-ZnO photocatalysts. The Z-scheme charge carrier pathway induced by the presence of Cs2O has emerged as the reason behind the efficient charge carrier separation and high photocatalytic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Singh S.; Sharma R.; Mehta B. R. Enhanced surface area, high Zn interstitial defects and band gap reduction in N-doped ZnO nanosheets coupled with BiVO 4 leads to improved photocatalytic performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 411, 321–330. 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.189. - DOI
-
- Wang C.-C.; Li J.-R.; Lv X.-L.; Zhang Y.-Q.; Guo G. Photocatalytic organic pollutants degradation in metal-organic frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2831–2867. 10.1039/c4ee01299b. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

