Multiplex Detection of Nucleic Acids Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Molecular Colorimetric 7-Segment Display
- PMID: 31460243
- PMCID: PMC6682049
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01097
Multiplex Detection of Nucleic Acids Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Molecular Colorimetric 7-Segment Display
Abstract
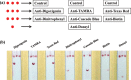
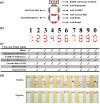
Nucleic acid analysis has become highly relevant for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics since the advent of isothermal amplification methods that do not require thermal cycling. In particular, recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) combined with lateral flow detection offers a rapid and simple solution for field-amenable low-resource nucleic acid testing. Expanding POC nucleic acid tests for the detection of multiple analytes is vital to improve diagnostic efficiency because increased multiplexing capacity enables higher information density combined with reduced assay time and costs. Here, we investigate expanding RPA POC detection by identifying a generic multiplex RPA format that can be combined with a generic multiplex lateral flow device (LFD) to enable binary and molecular encoding for the compaction of diagnostic data. This new technology relies on the incorporation of molecular labels to differentiate nucleic acid species spatially on a lateral flow membrane. In particular, we identified additional five molecular labels that can be incorporated during the RPA reaction for subsequent coupling with LFD detection. Combined with two previously demonstrated successful labels, we demonstrate potential to enable hepta-plex detection of RPA reactions coupled to multiplex LFD detection. When this hepta-plex detection is combined with binary and molecular encoding, an intuitive 7-segment output display can be produced. We note that in all experiments, we used an identical DNA template, except for the 5' label on the forward primer, to eliminate any effects of nucleic acid sequence amplification bias. Our proof-of-concept technology demonstration is highly relevant for developing information-compact POC diagnostics where space and time are premium commodities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Joanne Macdonald is the founder of and shareholder in diagnostics company BioCifer Pty. Ltd, which was not involved in the study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick assay for rapid detection of the Mycoplasma bovis.BMC Vet Res. 2018 Dec 20;14(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1703-x. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30572884 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of serotype-specific recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick assays for the diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype A, O and Asia1.BMC Vet Res. 2018 Nov 20;14(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1644-4. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30458768 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and visual detection of Lawsonia intracellularis with an improved recombinase polymerase amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick.BMC Vet Res. 2019 Mar 21;15(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1841-9. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 30898117 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinase polymerase amplification: Emergence as a critical molecular technology for rapid, low-resource diagnostics.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15(11):1475-89. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1090877. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 26517245 Review.
-
Exponential Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids and Assays for Proteins, Cells, Small Molecules, and Enzyme Activities: An EXPAR Example.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Sep 10;57(37):11856-11866. doi: 10.1002/anie.201712217. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29704305 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and pre-clinical evaluation of a Zika virus diagnostic for low resource settings.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 20;14:1214148. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1214148. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38053551 Free PMC article.
-
From saliva to SNP: non-invasive, point-of-care genotyping for precision medicine applications using recombinase polymerase amplification and giant magnetoresistive nanosensors.Lab Chip. 2022 May 31;22(11):2131-2144. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00233g. Lab Chip. 2022. PMID: 35537344 Free PMC article.
-
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification for monitoring hand-foot-and-mouth disease: current status and future implications.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Dec 25;192(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06899-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39720958 Review.
-
Current and Perspective Sensing Methods for Monkeypox Virus.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;9(10):571. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9100571. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Diagnostic Tests for the Detection of the Four Dengue Virus Serotypes in Clinically Relevant Matrices.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0279622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02796-22. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36682882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piepenburg O.; Williams C. H.; Stemple D. L.; Armes N. A. DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e20410.1371/journal.pbio.0040204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Kalsi S.; Valiadi M.; Tsaloglou M.-N.; Parry-Jones L.; Jacobs A.; Watson R.; Turner C.; Amos R.; Hadwen B.; Buse J.; Brown C.; Sutton M.; Morgan H. Rapid and sensitive detection of antibiotic resistance on a programmable digital microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3065–3075. 10.1039/c5lc00462d. - DOI - PubMed
- Szántó-Egész R.; Jánosi A.; Mohr A.; Szalai G.; Szabó E. K.; Micsinai A.; Sipos R.; Rátky J.; Anton I.; Zsolnai A. Breed-specific detection of mangalica meat in food products. Food. Anal. Method. 2016, 889–894. 10.1007/s12161-015-0261-0. - DOI
- Yehia N.; Arafa A.-S.; Abd El Wahed A.; El-Sanousi A. A.; Weidmann M.; Shalaby M. A. Development of reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for avian influenza H5N1 HA gene detection. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 223, 45–49. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
- James A.; Macdonald J. Recombinase polymerase amplification: emergence as a critical molecular technology for rapid, low-resource diagnostics. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1475–1489. 10.1586/14737159.2015.1090877. - DOI - PubMed
- Li J.; Macdonald J.; von Stetten F. Review: a comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2019, 144, 31–67. 10.1039/c8an01621f. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krõlov K.; Frolova J.; Tudoran O.; Suhorutsenko J.; Lehto T.; Sibul H.; Mäger I.; Laanpere M.; Tulp I.; Langel Ü. Sensitive and rapid detection of Chlamydia trachomatis by recombinase polymerase amplification directly from urine samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 127–135. 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
- Kersting S.; Rausch V.; Bier F. F.; von Nickisch-Rosenegk M. Rapid detection of Plasmodium falciparum with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow analysis. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 99.10.1186/1475-2875-13-99. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Mekuria T. A.; Zhang S.; Eastwell K. C. Rapid and sensitive detection of Little cherry virus 2 using isothermal reverse transcription-recombinase polymerase amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 205, 24–30. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.04.015. - DOI - PubMed
- Crannell Z. A.; Cabada M. M.; Richards-Kortum R.; White A. C.; Irani A.; Castellanos-Gonzalez A. Recombinase polymerase amplification-based assay to diagnose Giardia in stool samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 583–587. 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Chao C.-C.; Belinskaya T.; Zhang Z.; Ching W.-M. Development of recombinase polymerase amplification assays for detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi or Rickettsia typhi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e000388410.1371/journal.pntd.0003884. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Rosser A.; Rollinson D.; Forrest M.; Webster B. L. Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection. Parasit. Vectors. 2015, 8, 446.10.1186/s13071-015-1055-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Yang Y.; Qin X.; Wang G.; Jin J.; Shang Y.; Zhang Z. Development of an isothermoal amplification-based assay for rapid visual detection of an Orf virus. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 46.10.1186/s12985-016-0502-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Yang Y.; Qin X.; Sun Y.; Cong G.; Li Y.; Zhang Z. Development of Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017, 8403642.10.1155/2017/8403642. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tian L.; Sato T.; Niwa K.; Kawase M.; Tanner A. C.; Takahashi N. Rapid and sensitive PCR-dipstick DNA chromatography for multiplex analysis of the oral microbiota. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 180323.10.1155/2014/180323. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Blažková M.; Koets M.; Rauch P.; Amerongen A. Development of a nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassay for simultaneous detection of Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in food. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 867–874. 10.1007/s00217-009-1115-z. - DOI
- Noguera P.; Posthuma-Trumpie G. A.; van Tuil M.; van der Wal F. J.; de Boer A.; Moers A. P. H. A.; van Amerongen A. Carbon nanoparticles in lateral flow methods to detect genes encoding virulence factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 831–838. 10.1007/s00216-010-4334-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Blažková M.; Koets M.; Wichers J. H.; Amerongen A. v.; Fukal L.; Rauch P. Nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of pathogenic bacteria from food. Czech J. Food. Sci. 2009, 27, S350–S353. 10.17221/959-cjfs. - DOI
- Lattanzio V. M. T.; Nivarlet N.; Lippolis V.; Gatta S. D.; Huet A.-C.; Delahaut P.; Granier B.; Visconti A. Multiplex dipstick immunoassay for semi-quantitative determination of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 718, 99–108. 10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.060. - DOI - PubMed
- Kolosova A. Y.; De Saeger S.; Sibanda L.; Verheijen R.; Van Peteghem C. Development of a colloidal gold-based lateral-flow immunoassay for the rapid simultaneous detection of zearalenone and deoxynivalenol. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 2103–2107. 10.1007/s00216-007-1642-z. - DOI - PubMed
- Shim W. B.; Dzantiev B. B.; Eremin S. A.; Chung D. H. One-step simultaneous immunochromatographic strip test for multianalysis of ochratoxin a and zearalenone. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 83–92. - PubMed
- Huang Z.-B.; Xu Y.; Li L.-S.; Li Y.-P.; Zhang H.; He Q.-H. Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for the rapid simultaneous detection of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in wheat and maize. Food Control 2012, 28, 7–12. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.04.035. - DOI
- Xu Y.; Liu Y.; Wu Y.; Xia X.; Liao Y.; Li Q. Fluorescent probe-based lateral flow assay for multiplex nucleic acid detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5611–5614. 10.1021/ac5010458. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

