Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on a Functionalized Ionic Liquid and Helical Carbon Nanotubes for the Determination of Cardiac Troponin I
- PMID: 31460299
- PMCID: PMC6682139
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01152
Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on a Functionalized Ionic Liquid and Helical Carbon Nanotubes for the Determination of Cardiac Troponin I
Abstract
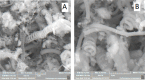
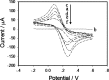
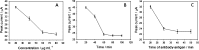
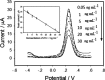
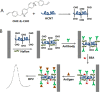
A label-free electrochemical immunosensor for cardiac troponin I was prepared by using a helical carbon nanotube-supported aldehyde-functionalized ionic liquid. Because of the good conductivity of ionic liquid and helical carbon nanotubes, high sensitivity of the immunosensor was obtained. Functionalized ionic liquid provided binding sites for antibody, which simplified the process of sensor construction. Cardiac troponin I was detected by this immunosensor with a linear range of 0.05-30 ng/mL and a detection limit of 0.03 ng/mL. The electrochemical immunosensor had satisfactory reproducibility, high sensitivity, and acceptable specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on β-Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Helical Carbon Nanotube and Ionic Liquid Containing Ferrocene and Aldehyde Groups.ACS Omega. 2019 Nov 20;4(23):20252-20256. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02559. eCollection 2019 Dec 3. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31815227 Free PMC article.
-
A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on aldehyde-terminated ionic liquid.Talanta. 2017 Dec 1;175:347-351. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28842001
-
A carbon nanotube screen-printed electrode for label-free detection of the human cardiac troponin T.Talanta. 2013 Dec 15;117:431-7. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.08.059. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Talanta. 2013. PMID: 24209364
-
Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Ionic Liquid Containing Dialdehyde As a Novel Linking Agent for the Antibody Immobilization.ACS Omega. 2018 Sep 30;3(9):11227-11232. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01298. Epub 2018 Sep 14. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30320258 Free PMC article.
-
The label-free immunosensor based on rhodium@palladium nanodendrites/sulfo group functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the sensitive analysis of carcino embryonic antigen.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 May 12;1007:61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.030. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29405989
Cited by
-
Functional Ionic Liquids Decorated Carbon Hybrid Nanomaterials for the Electrochemical Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 23;11(11):414. doi: 10.3390/bios11110414. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34821629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on nanomaterial-empowered electrochemical biosensors for the detection of cardiac troponin I.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 23;15(32):26473-26489. doi: 10.1039/d5ra04555j. eCollection 2025 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40703066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscale Technologies in Highly Sensitive Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 5;8:531. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00531. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32582663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroanalytical point-of-care detection of gold standard and emerging cardiac biomarkers for stratification and monitoring in intensive care medicine - a review.Mikrochim Acta. 2022 Mar 12;189(4):142. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05186-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35279780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Separation and enrichment of trace aflatoxin B1 in grains by magnetic nanomaterials based on SiO2@Fe3O4].Se Pu. 2022 Aug;40(8):694-703. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.03002. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 35903836 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Tan Y.; Wang Y.; Li M.; Ye X.; Wu T.; Li C. Enhanced photoelectrochemical immunosensing of cardiac troponin I based on energy transfer between N-acetyl-Lcysteine capped CdAgTe quantum dots and dodecahedral Au nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 741–746. 10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

