Pegvisomant in acromegaly: a multicenter real-life study in Argentina
- PMID: 31460622
- PMCID: PMC10528651
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000160
Pegvisomant in acromegaly: a multicenter real-life study in Argentina
Abstract
Objective: To describe the long term safety and efficacy of pegvisomant (PEGV), and the predictors of treatment response in patients with acromegaly in the real life setting.
Subjects and methods: We retrospectively reviewed the clinical, hormonal and radiological data of acromegalic patients treated with PEGV in 17 Argentine centers.
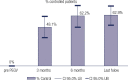
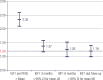
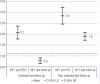
Results: Seventy-five patients (age range 22-77, 51 females) with acromegaly have been treated with PEGV for up to 118 months (median 27 months). Before PEGV, 97.3% of patients had been treated with medical therapy, surgery and/or radiotherapy, two patients had no previous treatment. At that time, all patients had an IGF-1 above the upper normal limit (ULN) (mean 2.4 x ULN ± 0.98, range 1.25-7). At diagnosis of acromegaly 84% presented macroadenomas, prior to PEGV only 23,5% of patients remained with tumor remnant > 1 cm, the remaining showed normal or less than 1 cm images. Disease control (IGF-1 ≤ 1.2 x ULN) was achieved in 62.9% of patients with a mean dose of 11.8 mg/day. Thirty-four patients (45%) received PEGV monotherapy, while 41 (55%) received combined therapy with either somatostatin analogues and/or cabergoline. Adverse events related to PEGV were: local injection site reaction in 5.3%, elevated liver enzymes in 9.3%, and tumor size growth in 9.8%. Pre-PEGV IGF-I level was the only predictor of treatment response: 2.1 x ULN vs 2.8 x ULN in controlled and uncontrolled patients respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: this long term experience indicates PEGV treatment was highly effective and safe in our series of Argentine patients with acromegaly refractory to standard therapies. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019;63(4):320-7.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: KD has received speaker fee from Novartis and Pfizer, advisory board fee from Sandoz. DK has received speaker fee from Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi. MM. is Medical Manager Oncology Novartis. GBNX is Medical Science Liaison Diabetes Sanofi. GR. has received speaker fee from Biosidus, Eli Lilly and Elea. GM has received speaker fee from Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi; and is principal investigator from Novartis. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Pegvisomant for acromegaly: does it always works?Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Aug 22;63(4):318-319. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000163. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31460621 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Melmed S. Medical progress: Acromegaly. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(24):2558-73. - PubMed
-
- Kauppinen-Mäkelin R, Sane T, Reunanen A, Välimäki MJ, Niskanen L, Markkanen H, et al. A nationwide survey of mortality in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(7):4081-6. - PubMed
-
- Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G. Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(1):102-52. - PubMed
-
- Holdaway IM, Rajasoorya RC, Gamble GD. Factors influencing mortality in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(2):667-74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
