A modelling framework for improved design and decision-making in drug development
- PMID: 31461440
- PMCID: PMC6713335
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220812
A modelling framework for improved design and decision-making in drug development
Abstract
The development of a new drug is an extremely high-risk enterprise. The attrition rates of development projects and the average costs for each launched product are daunting, and the completion of a development program requires a very long time horizon. These facts imply that there are huge potential gains, should one be able to improve efficiency and enhance decision-making capabilities. In this paper, we argue that substantial gains can be achieved by adapting a holistic view of drug development. Historically, too much planning, design and decision-making in the pharmaceutical development has been based on locally optimising separate parts of the development program, and too often important sources of uncertainty are ignored. We propose instead a model-based approach built on two essential pillars; (1) an integrated holistic view of the development program, including post-launch marketing and sales, with all parts evaluated simultaneously; (2) an explicit appreciation of all relevant sources of uncertainty. Computer simulations are utilised to evaluate the properties of the program options at hand, and to provide valuable quantitative decision support. Applications of this modelling approach have proven to add large value to development projects in terms of better program options being generated and more value-adding decisions taken.
Conflict of interest statement
SJW is a paid employee of Captario AB. There are no patents, products in development or further marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

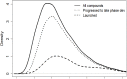
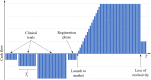
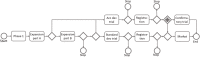
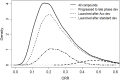

References
-
- FDA, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Novel Drug Approvals for 2018. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/developmentapprovalprocess/druginnovation/ucm5.... Source accessed: 20 Jan 2019.
-
- Mullard A. Industry R&D returns slip. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2016;15:7. - PubMed
-
- Deloitte. 2018. Unlocking R&D productivity: Measuring the return of pharmaceutical innovation 2018. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/life-sciences-and-health-care/arti.... Source accessed: 20 Jan 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

