Synthetic Essentiality of Metabolic Regulator PDHK1 in PTEN-Deficient Cells and Cancers
- PMID: 31461649
- PMCID: PMC6728083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.063
Synthetic Essentiality of Metabolic Regulator PDHK1 in PTEN-Deficient Cells and Cancers
Abstract
Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) is a tumor suppressor and bi-functional lipid and protein phosphatase. We report that the metabolic regulator pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase1 (PDHK1) is a synthetic-essential gene in PTEN-deficient cancer and normal cells. The PTEN protein phosphatase dephosphorylates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-activating protein (NKAP) and limits NFκB activation to suppress expression of PDHK1, a NF-κB target gene. Loss of the PTEN protein phosphatase upregulates PDHK1 to induce aerobic glycolysis and PDHK1 cellular dependence. PTEN-deficient human tumors harbor increased PDHK1, a biomarker of decreased patient survival. This study uncovers a PTEN-regulated signaling pathway and reveals PDHK1 as a potential target in PTEN-deficient cancers.
Keywords: NF-κB; NKAP; PDHK1; PTEN; cancer; metabolism; protein phosphatase; signaling; synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
T.G.B. is an advisor to Array Biopharma, Revolution Medicines, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Springworks, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals and receives research funding from Novartis and Revolution Medicines.
Figures

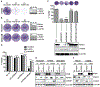
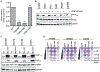


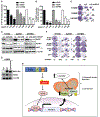
References
-
- Aoki Y, and Kao PN (1997). Cyclosporin A-sensitive calcium signaling represses NFkappaB activation in human bronchial epithelial cells and enhances NFkappaB activation in Jurkat T-cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 234, 424–431. - PubMed
-
- Berger N, Ben Bassat H, Klein BY, and Laskov R (2007). Cytotoxicity of NF-kappaB inhibitors Bay 11-7085 and caffeic acid phenethyl ester to Ramos and other human B-lymphoma cell lines. Exp. Hematol. 35, 1495–1509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA217882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008284/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224081/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 CA174497/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM136415/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM123159/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA169338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA218691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA128583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA204302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM118939/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA211052/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA108462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA209891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

