Value of virtual monochromatic spectral image of dual-layer spectral detector CT with noise reduction algorithm for image quality improvement in obese simulated body phantom
- PMID: 31462212
- PMCID: PMC6714289
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-019-0367-8
Value of virtual monochromatic spectral image of dual-layer spectral detector CT with noise reduction algorithm for image quality improvement in obese simulated body phantom
Abstract
Background: Dual-layer spectral detector CT (SDCT) may provide several theoretical advantages over pre-existing DECT approaches in terms of adjustment-free sampling number and dose modulation, beam hardening correction, and production spectral images by post-processing. In addition, by adopting noise reduction algorithm, high contrast resolution was expected even in low keV level. We surmised that this improvement would be beneficial to obese people. Therefore, our aim of study is to compare image quality of virtual monochromatic spectral images (VMI) and polychromatic images reconstructed from SDCT with different body size and radiation dose using anthropomorphic liver phantom.
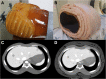
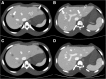
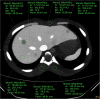
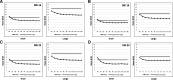
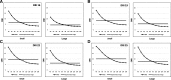
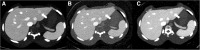
Methods: One small and one large size of body phantoms, each containing eight (four high- and four low-contrast) simulated focal liver lesions (FLLs) were scanned by SDCT (at 120 kVp) using different Dose Right Indexes (DRIs). VMI were reconstructed from spectral base images from 40 keV to 200 keV. Hybrid iterative reconstruction (iDose4) was used for polychromatic image reconstruction. Image noise and contrast to noise ratio (CNR) were compared. Five radiologists independently rated lesion conspicuity, diagnostic acceptability and subjective noise level in every image sets, and determined optimal keV level in VMI.
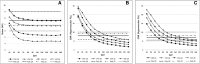
Results: Compare with conventional polychromatic images, VMI showed superior CNR at low keV level regardless of phantom size at every examined DRIs (Ps < 0.05). As body size increased, VMI had more gradual CNR decrease and noise increase than conventional polychromatic images. For low contrast FLLs in large phantom, lesion conspicuities at low radiation dose levels (DRI 16 and 19) were significantly increased in VMI (Ps < 0.05). Subjective image noise and diagnostic acceptabilities were significantly improved at VMI in both phantom size.
Conclusions: VMI of dual-layer spectral detector CT with noise reduction algorithm provides improved CNR, noise reduction, and better subjective image quality in imaging of obese simulated liver phantom compared with polychromatic images. This may hold promise for improving detection of liver lesions and improved imaging of obese patients.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Dual-energy; Liver; Obesity; Phantom; Spectral detector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virtual monochromatic imaging in dual-source dual-energy CT: radiation dose and image quality.Med Phys. 2011 Dec;38(12):6371-9. doi: 10.1118/1.3658568. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 22149820 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-layer spectral detector CT for contrast agent concentration, dose and injection rate reduction: Utility in imaging of the superior mesenteric artery.Eur J Radiol. 2022 May;150:110246. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110246. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35294908
-
Optimal Kiloelectron Volt for Noise-Optimized Virtual Monoenergetic Images of Dual-Energy Pediatric Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography: Preliminary Results.Korean J Radiol. 2019 Feb;20(2):283-294. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.0507. Korean J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30672168 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-energy CT applications on liver imaging: what radiologists and radiographers should know? A systematic review.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024 Nov;49(11):3811-3823. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04380-y. Epub 2024 May 30. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024. PMID: 38811447
-
Spectral detector CT applications in advanced liver imaging.Br J Radiol. 2021 Jul 1;94(1123):20201290. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201290. Epub 2021 May 28. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34048285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards Personalised Contrast Injection: Artificial-Intelligence-Derived Body Composition and Liver Enhancement in Computed Tomography.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 24;11(3):159. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030159. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33668286 Free PMC article.
-
Low dose of contrast agent and low radiation liver computed tomography with deep-learning-based contrast boosting model in participants at high-risk for hepatocellular carcinoma: prospective, randomized, double-blind study.Eur Radiol. 2023 May;33(5):3660-3670. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09520-4. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36934202 Clinical Trial.
-
Application of Dual-Energy Spectral Computed Tomography in Bone Mineral Density Measurement: Phantom and Clinical Research.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Aug 29;15:6887-6896. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S381857. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 36061965 Free PMC article.
-
Use of dual-energy CT for renal mass assessment.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jun;31(6):3721-3733. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07426-z. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33210200 Review.
-
Comparative analysis of automatic segmentation of esophageal cancer using 3D Res-UNet on conventional and 40-keV virtual mono-energetic CT Images: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 17;11:e15707. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15707. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37483982 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Darras KE, McLaughlin PD, Kang H, Black B, Walshe T, Chang SD, Harris AC, Nicolaou S. Virtual monoenergetic reconstruction of contrast-enhanced dual energy CT at 70keV maximizes mural enhancement in acute small bowel obstruction. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(5):950–956. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.02.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

