Exploration of Copper-Cysteamine Nanoparticles as a New Type of Agents for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation
- PMID: 31462378
- PMCID: PMC6731549
- DOI: 10.1166/jbn.2019.2829
Exploration of Copper-Cysteamine Nanoparticles as a New Type of Agents for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation
Abstract
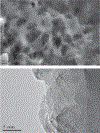
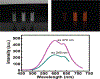
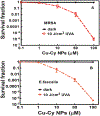
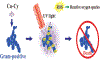
Copper-cysteamine (Cu-Cy) nanoparticles (NPs) are a new type of sensitizers that can be activated by UV light, X-rays, microwaves and ultrasound to produce reactive oxygen species for cancer treatment. Here, for the first time, we explored Cu-Cy NPs for bacteria inactivation by treating gram-positive bacteria (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis) and gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii), respectively. The results show that Cu-Cy NPs are very effective in killing gram-positive bacteria but are quite limited in killing gram-negative bacteria yet. The major killing mechanism is cell damage by singlet oxygen and Cu-Cy NPs are potential agents for bacteria inactivation.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

