Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive lacosamide in pediatric patients with focal seizures
- PMID: 31462582
- PMCID: PMC6808531
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008126
Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive lacosamide in pediatric patients with focal seizures
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive lacosamide in children and adolescents with uncontrolled focal (partial-onset) seizures.
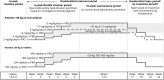
Methods: In this double-blind trial (SP0969; NCT01921205), patients (age ≥4-<17 years) with uncontrolled focal seizures were randomized (1:1) to adjunctive lacosamide/placebo. After a 6-week titration, patients who reached the target dose range for their weight (<30 kg: 8-12 mg/kg/d oral solution; ≥30-<50 kg: 6-8 mg/kg/d oral solution; ≥50 kg: 300-400 mg/d tablets) entered a 10-week maintenance period. The primary outcome was change in focal seizure frequency per 28 days from baseline to maintenance.
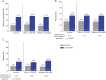
Results: Three hundred forty-three patients were randomized; 306 (lacosamide 152 of 171 [88.9%]; placebo 154 of 172 [89.5%]) completed treatment (titration and maintenance). Adverse events (AEs) were the most common reasons for discontinuation during treatment (lacosamide 4.1%; placebo 5.8%). From baseline to maintenance, percent reduction in focal seizure frequency per 28 days for lacosamide (n = 170) vs placebo (n = 168) was 31.7% (p = 0.0003). During maintenance, median percent reduction in focal seizure frequency per 28 days was 51.7% for lacosamide and 21.7% for placebo. Fifty percent responder rates (≥50% reduction) were 52.9% and 33.3% (odds ratio 2.17, p = 0.0006). During treatment, treatment-emergent AEs were reported by 67.8% lacosamide-treated patients (placebo 58.1%), most commonly (≥10%) somnolence (14.0%, placebo 5.2%) and dizziness (10.5%, placebo 3.5%).
Conclusions: Adjunctive lacosamide was efficacious in reducing seizure frequency and generally well tolerated in patients (age ≥4-<17 years) with focal seizures.
Clinicaltrialsgov identifier: NCT01921205.
Classification of evidence: This trial provides Class I evidence that for children and adolescents with uncontrolled focal seizures, adjunctive lacosamide reduces seizure frequency.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Verrotti A, Loiacono G, Coppola G, Spalice A, Mohn A, Chiarelli F. Pharmacotherapy for children and adolescents with epilepsy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2011;12:175–194. - PubMed
-
- Rogawski MA, Tofighy A, White HS, Matagne A, Wolff C. Current understanding of the mechanism of action of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide. Epilepsy Res 2015;110:189–205. - PubMed
-
- Cawello W. Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of lacosamide. Clin Pharmacokinet 2015;54:901–914. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Menachem E, Biton V, Jatuzis D, Abou-Khalil B, Doty P, Rudd GD. Efficacy and safety of oral lacosamide as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia 2007;48:1308–1317. - PubMed
-
- Chung S, Sperling MR, Biton V, et al. . Lacosamide as adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures: a randomized controlled trial. Epilepsia 2010;51:958–967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
