Automated Insulin Delivery Algorithms
- PMID: 31462875
- PMCID: PMC6695267
- DOI: 10.2337/ds18-0100
Automated Insulin Delivery Algorithms
Abstract
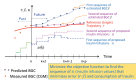
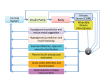
IN BRIEF Automated insulin delivery (AID; also known as artificial pancreas) has improved the regulation of blood glucose concentrations, reduced the frequency of hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic episodes, and improved the quality of life of people with diabetes and their families. Three different types of algorithms-proportional-integral-derivative control, model predictive control, and fuzzy-logic knowledge-based systems-have been used in AID control systems. This article will highlight the foundations of these algorithms and discuss their strengths and limitations. Multivariable artificial pancreas and dual-hormone (insulin and glucagon) systems will be introduced.
Figures
References
-
- Albisser AM, Leibel BS, Ewart TG, Davidovac Z, Botz CK, Zingg W. An artificial endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 1974;23:389–396 - PubMed
-
- Medtronic Diabetes MiniMed 670G Insulin Pump System. Available from www.medtronicdiabetes.com/products/minimed-670g-insulin-pump-system#system. Accessed 22 February 2019
-
- Ly TT, Roy A, Grosman B, et al. . Day and night closed-loop control using the integrated Medtronic hybrid closed-loop system in type 1 diabetes at diabetes camp. Diabetes Care 2015;38:1205–1211 - PubMed
-
- Hovorka R, Allen JM, Elleri D, et al. . Manual closed-loop insulin delivery in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a phase 2 randomised crossover trial. Lancet 2010;375:743–751 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources