Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor suppresses HPV E6-expressing HNSCC progression by mediating NF-κB and Akt pathways
- PMID: 31462893
- PMCID: PMC6708138
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0942-7
Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor suppresses HPV E6-expressing HNSCC progression by mediating NF-κB and Akt pathways
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most common cancer worldwide and human papillomavirus (HPV) has been increasingly recognized as a pathogenic factor for the initiation and development of HNSCC. E6 oncogene, an essential component of the HPV 16 virus, acts as a leading cause of the malignant transformation of cancer cells. Therefore, investigating the biological effect and potential mechanisms of E6 oncogene on HNSCC cells and exploring potential therapeutic methods is of great value.
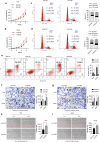
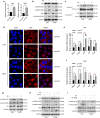
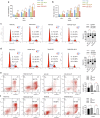
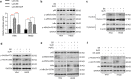
Methods: MTT assay, cell cycle analysis, and apoptosis assay were implemented to detect the biological effect of E6 oncogene on the growth of HNSCC cells. Wound healing assay and transwell assay were used to evaluate the role of E6 in the migration and invasion of HNSCC cells. Western blot and immunofluorescence assay were adopted to explore the regulatory mechanisms underlying E6-induced HNSCC progression. Then, exogenous secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) was added into the cell culture to investigate whether it could maintain its tumor suppressor effect on E6-expressing HNSCC cells.
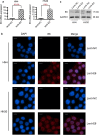
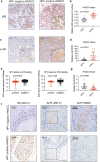
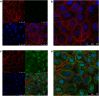
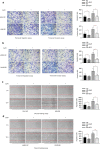
Results: HPV E6 oncogene could promote the proliferation, cell cycle period, apoptosis resistance, migration and invasion of HNSCC cells by activating NF-κB and Akt pathways. Immunohistochemical analysis conducted on HNSCC tissues illustrated that SLPI was further downregulated in HPV positive HNSCC compared to HNSCC without HPV infection. Exogenous SLPI significantly inhibited HPV E6-mediated malignant phenotypes in HNSCC cells by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and Akt and signaling pathways.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that E6 oncogene led to the malignant transformation of HNSCC cells by regulating multiple pathways. SLPI could reverse the effect of E6 oncogene on HNSCC, implying that the functional inhibition of E6 by SLPI may be exploited as an attractive therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Akt pathway; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Human papillomavirus; NF-κB; Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liberation of functional p53 by proteasome inhibition in human papilloma virus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells promotes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.Cell Cycle. 2013 Mar 15;12(6):923-34. doi: 10.4161/cc.23882. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23421999 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus infection in head and neck cancer: the role of the secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor.Oncol Rep. 2013 May;29(5):1962-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2327. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23467841 Free PMC article.
-
Radioimmunotherapy of experimental head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with E6-specific antibody using a novel HPV-16 positive HNSCC cell line.Head Neck Oncol. 2011 Feb 12;3(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1758-3284-3-9. Head Neck Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21314983 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) in cancer pathophysiology: Mechanisms of action and clinical implications.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154633. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154633. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37356220 Review.
-
Expression and molecular regulation of non-coding RNAs in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 29;13:1122982. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1122982. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37064141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Assessment of Biological and Functional Properties of Potential Probiotic Strains Isolated from Commercial and Dairy Sources.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 24;13(5):970. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13050970. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431142 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in HPV-Driven Head and Neck Carcinogenesis: Therapeutic Implications.Biology (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;12(5):672. doi: 10.3390/biology12050672. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPV16 E6 enhances the radiosensitivity in HPV-positive human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-27a-3p/SMG1 axis.Infect Agent Cancer. 2021 Aug 13;16(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13027-021-00397-w. Infect Agent Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34389030 Free PMC article.
-
The secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) in pathophysiology of non-communicable diseases: Evidence from experimental studies to clinical applications.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 17;10(2):e24550. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24550. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of human papillomavirus in cancers: oncogenic mechanisms and clinical use.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 24;10(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02083-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39856040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Munoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjose S, Herrero R, Castellsague X, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ. International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical Cancer Study G: epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(6):518–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021641. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

