Artificial intelligence and machine learning in spine research
- PMID: 31463458
- PMCID: PMC6686793
- DOI: 10.1002/jsp2.1044
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in spine research
Abstract
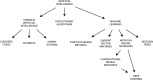
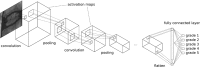
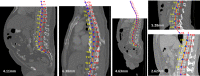
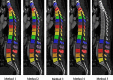
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques are revolutionizing several industrial and research fields like computer vision, autonomous driving, natural language processing, and speech recognition. These novel tools are already having a major impact in radiology, diagnostics, and many other fields in which the availability of automated solution may benefit the accuracy and repeatability of the execution of critical tasks. In this narrative review, we first present a brief description of the various techniques that are being developed nowadays, with special focus on those used in spine research. Then, we describe the applications of AI and ML to problems related to the spine which have been published so far, including the localization of vertebrae and discs in radiological images, image segmentation, computer-aided diagnosis, prediction of clinical outcomes and complications, decision support systems, content-based image retrieval, biomechanics, and motion analysis. Finally, we briefly discuss major ethical issues related to the use of AI in healthcare, namely, accountability, risk of biased decisions as well as data privacy and security, which are nowadays being debated in the scientific community and by regulatory agencies.
Keywords: artificial neural networks; deep learning; ethical implications; outcome prediction; segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article. Author contributionsF.G.: literature analysis, manuscript preparation and revision; G.C.: literature analysis, manuscript revision; T.B.: literature analysis, manuscript preparation and revision.
Figures






References
-
- Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. IBM J Res Dev. 1959;3:210‐229.
-
- Nilsson NJ. The Quest for Artificial Intelligence. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
-
- He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Piscataway, NJ: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE); 2016. ArXiv Preprint arXiv:1512.03385.
-
- Slate DJ, Atkin LR. Chess 4.5—the Northwestern University chess program In: Frey PW, ed. Chess Skill in Man and Machine. New York, NY: Springer; 1983.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

