Radiation mitigation of the intestinal acute radiation injury in mice by 1-[(4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl]-4-phenylpiperazine
- PMID: 31464098
- PMCID: PMC6954722
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.19-0136
Radiation mitigation of the intestinal acute radiation injury in mice by 1-[(4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl]-4-phenylpiperazine
Abstract
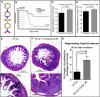
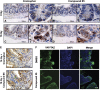
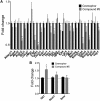
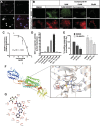
The objective of the study was to identify the mechanism of action for a radiation mitigator of the gastrointestinal (GI) acute radiation syndrome (ARS), identified in an unbiased high-throughput screen. We used mice irradiated with a lethal dose of radiation and treated with daily injections of the radiation mitigator 1-[(4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl]-4-phenylpiperazine to study its effects on key pathways involved in intestinal stem cell (ISC) maintenance. RNASeq, quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry were performed to identify pathways engaged after drug treatment. Target validation was performed with competition assays, reporter cells, and in silico docking. 1-[(4-Nitrophenyl)sulfonyl]-4-phenylpiperazine activates Hedgehog signaling by binding to the transmembrane domain of Smoothened, thereby expanding the ISC pool, increasing the number of regenerating crypts and preventing the GI-ARS. We conclude that Smoothened is a target for radiation mitigation in the small intestine that could be explored for use in radiation accidents as well as to mitigate normal tissue toxicity during and after radiotherapy of the abdomen.
Keywords: acute radiation syndrome; developmental signaling; intestinal stem cells; radiation.
© 2019 The Authors. Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Warren S, Bowers JZ. The acute radiation syndrome in man. Ann Intern Med. 1950;32:207‐216. - PubMed
-
- Weisdorf D, Chao N, Waselenko JK, et al. Acute radiation injury: contingency planning for triage, supportive care, and transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12:672‐682. - PubMed
-
- Withers HR, Elkind MM. Radiosensitivity and fractionation response of crypt cells of mouse jejunum. Radiat Res. 1969;38:598‐613. - PubMed
-
- Withers HR, Elkind MM. Microcolony survival assay for cells of mouse intestinal mucosa exposed to radiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1970;17:261‐267. - PubMed
-
- Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt‐villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459:262‐265. - PubMed

