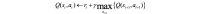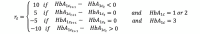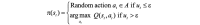A Reinforcement Learning-Based Method for Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Exploratory Study
- PMID: 31464196
- PMCID: PMC6737889
- DOI: 10.2196/12905
A Reinforcement Learning-Based Method for Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Exploratory Study
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is characterized by chronic insulin deficiency and consequent hyperglycemia. Patients with T1DM require long-term exogenous insulin therapy to regulate blood glucose levels and prevent the long-term complications of the disease. Currently, there are no effective algorithms that consider the unique characteristics of T1DM patients to automatically recommend personalized insulin dosage levels.
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop and validate a general reinforcement learning (RL) framework for the personalized treatment of T1DM using clinical data.
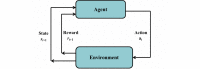
Methods: This research presents a model-free data-driven RL algorithm, namely Q-learning, that recommends insulin doses to regulate the blood glucose level of a T1DM patient, considering his or her state defined by glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, body mass index, engagement in physical activity, and alcohol usage. In this approach, the RL agent identifies the different states of the patient by exploring the patient's responses when he or she is subjected to varying insulin doses. On the basis of the result of a treatment action at time step t, the RL agent receives a numeric reward, positive or negative. The reward is calculated as a function of the difference between the actual blood glucose level achieved in response to the insulin dose and the targeted HbA1c level. The RL agent was trained on 10 years of clinical data of patients treated at the Mass General Hospital.
Results: A total of 87 patients were included in the training set. The mean age of these patients was 53 years, 59% (51/87) were male, 86% (75/87) were white, and 47% (41/87) were married. The performance of the RL agent was evaluated on 60 test cases. RL agent-recommended insulin dosage interval includes the actual dose prescribed by the physician in 53 out of 60 cases (53/60, 88%).
Conclusions: This exploratory study demonstrates that an RL algorithm can be used to recommend personalized insulin doses to achieve adequate glycemic control in patients with T1DM. However, further investigation in a larger sample of patients is needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Q-learning; T1DM; diabetes treatment; insulin dose prescription; machine learning; reinforcement learning; type 1 diabetes mellitus.
©Mahsa Oroojeni Mohammad Javad, Stephen Olusegun Agboola, Kamal Jethwani, Abe Zeid, Sagar Kamarthi. Originally published in JMIR Diabetes (http://diabetes.jmir.org), 28.08.2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. [2019-04-22]. Statistics About Diabetes: Overall Numbers, Diabetes and Prediabetes http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/statistics/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [2019-04-22]. CDC Newsroom https://www.cdc.gov/media/pressrel/2010/r101022.html.
-
- Martinez-Millana A, Jarones E, Fernandez-Llatas C, Hartvigsen G, Traver V. App features for type 1 diabetes support and patient empowerment: systematic literature review and benchmark comparison. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Nov 21;6(11):e12237. doi: 10.2196/12237. http://mhealth.jmir.org/2018/11/e12237/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. [2019-04-22]. Kidney Disease Statistics for the United States http://www.niddk.nih.gov/healthinformation/healthtopics/kidneydisease/ki....
-
- The United States Renal Data System. [2019-04-22]. 2016 Annual Data Report https://www.usrds.org/adr.aspx.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous