Impact of medicines regulatory risk communications in the UK on prescribing and clinical outcomes: Systematic review, time series analysis and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31465123
- PMCID: PMC7098864
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.14104
Impact of medicines regulatory risk communications in the UK on prescribing and clinical outcomes: Systematic review, time series analysis and meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;86(9):1894. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14497. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33464570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: Regulatory risk communications are important to ensure medication safety, but their impact is poorly understood. The aim was to quantify the impact of UK risk communications on medication use and other outcomes.
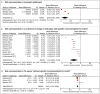
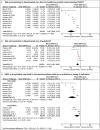
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of studies reporting prescribing/health outcome data relevant to UK regulatory risk communication. Data were reanalysed using interrupted time series regression 12 months after each regulatory intervention. Mean changes were pooled using random-effects generic inverse variance examining the following subgroups: drug withdrawals; restrictions/changes in indications; be aware messages without specific recommendations for action; communication via direct healthcare practitioner communications; communication via drug bulletins.
Results: Of 11 466 articles screened, 40 studies examining 25 UK regulatory risk communications were included. Product withdrawals, restriction in indications and be aware communications were associated with relative mean changes of -78% (95% confidence interval [CI] -60 to -96%), -34% (95% confidence interval [CI] -12 to -55%) and -11% (95%CI -8 to -15%) in targeted drug prescribing respectively. Direct healthcare professional communications were associated with relative mean changes of -47% (95%CI -27 to -68%) compared to -13% (95%CI -6 to -20%) for drug bulletins. Of 7 studies examining unique health outcomes related to the safety concern, risk communications were associated with a mean -10% (95%CI -3 to -16%) decrease in intended and a 7% (95%CI 4 to 10%) increase in unintended health outcomes.
Discussion: UK regulatory risk communications were associated with significant changes in targeted prescribing and potential changes in clinical outcomes. Further research is needed to systematically study the impact of regulatory interventions.
Keywords: clinical pharmacology; drug regulation; drug safety; epidemiology; pharmacovigilance; public health.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
No approvals were required to conduct this study as it uses published data.
The views expressed in this article are the personal views of the author(s) and may not be not be understood or quoted as reflecting the views of any particular organisation.
Figures

Comment in
-
Measuring the impact of risk communications: Robust analytical approaches are key.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;86(4):635-636. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14222. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32064646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta‐analysis of prospective studies. JAMA. 1998;279(15):1200‐1205. - PubMed
-
- Barnett K, Mercer SW, Norbury M, Watt G, Wyke S, Guthrie B. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross‐sectional study. Lancet. 2012;380(9836):37‐43. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency. PRAC recommends new measures to avoid valproate exposure during pregnancy. 09/02/2018. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/prac-recommends-new-measures-avoid-val... .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

