Examining inequalities in access to delivery by caesarean section in Nigeria
- PMID: 31465505
- PMCID: PMC6715280
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221778
Examining inequalities in access to delivery by caesarean section in Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Maternal deaths are far too common in Nigeria, and this is in part due to lack of access to lifesaving emergency obstetric care, especially among women in the poorest strata in Nigeria. Data on the extent of inequality in access to such lifesaving intervention could convince policymakers in developing an appropriate intervention. This study examines inequality in access to births by caesarean section in Nigeria.
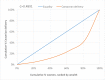
Methods: Data for 20,468 women who gave birth in the five years preceding 2013 Nigerian Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) were used for this study. Inequality in caesarean delivery was assessed using the concentration curve and multiple logistic regression models.
Results: There was a high concentration in the utilisation of caesarean section among the women in the relatively high wealth quintile. Overall, delivery by caesarean section was 2.1%, but the rate was highest among women who had higher education and belonged to the richest wealth quintile (13.6%) and lowest among women without formal education and who belonged to the poorest wealth quintile (0.4%). Belonging to the poorest wealth quintile and having no formal education were associated with lower odds of having delivery by caesarean section.
Conclusion: In conclusion, women in the richest households are within the WHO's recommended level of 10-15% for caesarean birth utilisation, but women in the poorest households are so far away from the recommended rate. Equity in healthcare is still a promise, its realisation will entail making care available to those in need not only those who can afford it.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, UNICEF. Trends in maternal mortality: 1990 to 2013: estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, The World Bank and the United Nations Population Division; 2014.
-
- Dahlgren G, Whitehead M. European strategies for tackling social inequities in health: Levelling up Part 2. Copenhagen: World Health Organization; 2006.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical