Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists against Hepatoblastoma
- PMID: 31466222
- PMCID: PMC6770178
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11091258
Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists against Hepatoblastoma
Abstract
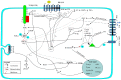
Hepatoblastoma (HB) is the most common malignant liver tumor that occurs during childhood. The prognosis of children with HB is favorable when a complete surgical resection of the tumor is possible, but for high-risk patients, the prognosis is much worse. New anti-HB strategies must be urgently developed. The undecapeptide substance P (SP) after binding to the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R), regulates cancer cell proliferation, exerts an antiapoptotic effect, induces cell migration for invasion/metastasis, and triggers endothelial cell proliferation for neoangiogenesis. HB samples and cell lines overexpress NK-1R (the truncated form) and SP elicits HB cell proliferation. One of these strategies could be the use of non-peptide NK-1R antagonists. These antagonists exert, in a concentration-dependent manner, an antiproliferative action against HB cells (inhibit cell proliferation and induce the death of HB cells by apoptosis). NK-1R antagonists exerted a dual effect in HB: Decreased both tumor volume and angiogenic activity. Thus, the SP/NK-1R system is an important target in the HB treatment and NK-1R antagonists could act as specific drugs against HB cells. In this review, we update and discuss the use of NK-1R antagonists in the treatment of HB.
Keywords: NK-1 receptor; angiogenesis; antitumor; apoptosis; aprepitant; hepatoblastoma; substance P.
Conflict of interest statement
USPTO Application no. 20090012086 “Use of non-peptidic NK-1 receptor antagonists for the production of apoptosis in tumor cells” (Miguel Muñoz). No conflict of interest (Marisa Rosso and Rafael Coveñas).
Figures
References
-
- Meyers R.L., Maibach R., Hiyama E., Häberle B., Krailo M., Rangaswami A., Aronson D.C., Malogolowkin M.H., Perilongo G., von Schweinitz D., et al. Risk-stratified staging in paediatric hepatoblastoma: A unified analysis from the children’s hepatic tumors international collaboration. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:122–131. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30598-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muñoz M., Rosso M., Robles-Frías M.J., Salinas-Martín M.V., Coveñas R. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human melanoma and is involved in the antitumor action of the NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant on melanoma cell lines. Lab. Investig. 2010;90:1259–1269. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.92. - DOI - PubMed

