Systematical Analysis of the Protein Targets of Lactoferricin B and Histatin-5 Using Yeast Proteome Microarrays
- PMID: 31466342
- PMCID: PMC6747642
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20174218
Systematical Analysis of the Protein Targets of Lactoferricin B and Histatin-5 Using Yeast Proteome Microarrays
Abstract
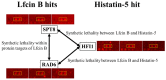
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have potential antifungal activities; however, their intracellular protein targets are poorly reported. Proteome microarray is an effective tool with high-throughput and rapid platform that systematically identifies the protein targets. In this study, we have used yeast proteome microarrays for systematical identification of the yeast protein targets of Lactoferricin B (Lfcin B) and Histatin-5. A total of 140 and 137 protein targets were identified from the triplicate yeast proteome microarray assays for Lfcin B and Histatin-5, respectively. The Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis showed that Lfcin B targeted more enrichment categories than Histatin-5 did in all GO biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components. This might be one of the reasons that Lfcin B has a lower minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) than Histatin-5. Moreover, pairwise essential proteins that have lethal effects on yeast were analyzed through synthetic lethality. A total of 11 synthetic lethal pairs were identified within the protein targets of Lfcin B. However, only three synthetic lethal pairs were identified within the protein targets of Histatin-5. The higher number of synthetic lethal pairs identified within the protein targets of Lfcin B might also be the reason for Lfcin B to have lower MIC than Histatin-5. Furthermore, two synthetic lethal pairs were identified between the unique protein targets of Lfcin B and Histatin-5. Both the identified synthetic lethal pairs proteins are part of the Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase (SAGA) protein complex that regulates gene expression via histone modification. Identification of synthetic lethal pairs between Lfcin B and Histatin-5 and their involvement in the same protein complex indicated synergistic combination between Lfcin B and Histatin-5. This hypothesis was experimentally confirmed by growth inhibition assay.
Keywords: Histatin-5; Lactoferricin B (Lfcin B); antifungal activity; antimicrobial peptides (AMPs); proteome microarray; synergy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Scorzoni L., de Paula E.S.A.C., Marcos C.M., Assato P.A., de Melo W.C., de Oliveira H.C., Costa-Orlandi C.B., Mendes-Giannini M.J., Fusco-Almeida A.M. Antifungal Therapy: New Advances in the Understanding and Treatment of Mycosis. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:36. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

