Protein biomarkers of neural system
- PMID: 31467504
- PMCID: PMC6712353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2019.03.001
Protein biomarkers of neural system
Abstract
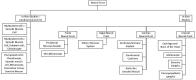
The utilization of biomarkers for in vivo and in vitro research is growing rapidly. This is mainly due to the enormous potential of biomarkers in evaluating molecular and cellular abnormalities in cell models and in tissue, and evaluating drug responses and the effectiveness of therapeutic intervention strategies. An important way to analyze the development of the human body is to assess molecular markers in embryonic specialized cells, which include the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Neuronal development is controlled through the gene networks in the neural crest and neural tube, both components of the ectoderm. The neural crest differentiates into several different tissues including, but not limited to, the peripheral nervous system, enteric nervous system, melanocyte, and the dental pulp. The neural tube eventually converts to the central nervous system. This review provides an overview of the differentiation of the ectoderm to a fully functioning nervous system, focusing on molecular biomarkers that emerge at each stage of the cellular specialization from multipotent stem cells to completely differentiated cells. Particularly, the otic placode is the origin of most of the inner ear cell types such as neurons, sensory hair cells, and supporting cells. During the development, different auditory cell types can be distinguished by the expression of the neurogenin differentiation factor1 (Neuro D1), Brn3a, and transcription factor GATA3. However, the mature auditory neurons express other markers including βIII tubulin, the vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT1), the tyrosine receptor kinase B and C (Trk B, C), BDNF, neurotrophin 3 (NT3), Calretinin, etc.
Keywords: Biomarker; Differentiation; Nervous system; Neural system; Otic placode; Stem cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The development of the vertebrate inner ear.Mech Dev. 1998 Feb;71(1-2):5-21. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(97)00155-x. Mech Dev. 1998. PMID: 9507049 Review.
-
Dual embryonic origin of the mammalian otic vesicle forming the inner ear.Development. 2011 Dec;138(24):5403-14. doi: 10.1242/dev.069849. Development. 2011. PMID: 22110056 Free PMC article.
-
Neural tube-ectoderm interactions are required for trigeminal placode formation.Development. 1997 Nov;124(21):4287-95. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.21.4287. Development. 1997. PMID: 9334277
-
Pax3-expressing trigeminal placode cells can localize to trunk neural crest sites but are committed to a cutaneous sensory neuron fate.Dev Biol. 2002 Sep 15;249(2):219-36. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0767. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12221003
-
Cannabinoid receptor signaling in progenitor/stem cell proliferation and differentiation.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):633-50. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 24076098 Review.
Cited by
-
KDM2B and its peptides promote the stem cells from apical papilla mediated nerve injury repair in rats by intervening EZH2 function.Cell Prolif. 2025 Feb;58(2):e13756. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13756. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 39358887 Free PMC article.
-
Differential genetic mutations of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm-derived tumors in TCGA database.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Dec 11;20(1):595. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01678-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33308219 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based proteomic characterization of the middle-aged mouse brain for animal model research of neuromuscular diseases.Eur J Transl Myol. 2023 Aug 3;33(3):11553. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2023.11553. Eur J Transl Myol. 2023. PMID: 37545360 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of Proangiogenic Molecules and Terminal Complement Complex C5b-9 in the Crown of Circulating sEVs in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastomas: Relationship with Tumor Molecular Characteristics.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 18;47(2):132. doi: 10.3390/cimb47020132. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996852 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Treat and Model Alzheimer's Disease.Stem Cells Int. 2021 May 26;2021:5511630. doi: 10.1155/2021/5511630. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34122554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anbuhl K.L., Uhler K.M., Werner L.A., Tollin D.J. 2016. Early Development of the Human Auditory System. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

