A Rare Case of New-Onset Ulcerative Colitis following Initiation of Secukinumab
- PMID: 31467555
- PMCID: PMC6701396
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2975631
A Rare Case of New-Onset Ulcerative Colitis following Initiation of Secukinumab
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "A Rare Case of New-Onset Ulcerative Colitis following Initiation of Secukinumab".Case Rep Med. 2019 Nov 20;2019:3689298. doi: 10.1155/2019/3689298. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Med. 2019. PMID: 31827522 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Secukinumab is an IgG monoclonal antibody widely used for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. Recently, there has been increasing controversy regarding potential adverse effects of the drug especially in those with underlying inflammatory bowel disease. We present the case of a young male patient who developed severe new-onset ulcerative colitis following initiation of secukinumab for psoriasis, with excellent response and rapid resolution of symptoms with infliximab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
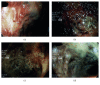
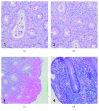
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

