Cardiovascular risk and obesity
- PMID: 31467596
- PMCID: PMC6712750
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-019-0468-0
Cardiovascular risk and obesity
Abstract
Background: This is an overview of the mechanisms of obesity and its relation to cardiovascular risks, describing the available treatment options to manage this condition.
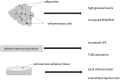
Main body: The pathogenesis of obesity includes the balance between calories consumed and energy expenditure followed by the maintenance of body weight. Diet, physical activity, environmental, behavioral and physiological factors are part of the complex process of weight loss, since there are several hormones and peptides involved in regulation of appetite, eating behavior and energy expenditure. The cardiovascular complications associated to obesity are also driven by processes involving hormones and peptides and which include inflammation, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, coronary calcification, activation of coagulation, renin angiotensin or the sympathetic nervous systems. Pharmacological treatments are often needed to insure weight loss and weight maintenance as adjuncts to diet and physical activity in people with obesity and overweight patients.
Conclusion: To accomplish satisfactory goals, patients and physicians seek for weight loss, weight maintenance and improvement of the risk factors associated to this condition, especially cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Clinical assessment; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsFF has served as steering committee member for Novartis and Astra Zeneca, and reports having received research grants, lecture fees, and consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Sanofi-Aventis, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Amgen, Biolab, Ache, EMS, and Merck. CC has served as advisory board for Eurofarma and Novo NordisK, and reports having received research grants from AstraZeneca, Sanofi-Aventis, Novo Nordisk, Eurofarma, Fractyl, Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Abbvie. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Poirier P. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 american heart association scientific statement on obesity and heart disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2006;113(6):898–918. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet—obesity and overweight. 2018. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Vassallo J. Pathogenesis of obesity. J Malta Coll Pharm Pract. 2007;12:19–22.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

