Supporting elderly people with cognitive impairment during and after hospital stays with intersectoral care management: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31470912
- PMCID: PMC6716860
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-019-3636-5
Supporting elderly people with cognitive impairment during and after hospital stays with intersectoral care management: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The sectorization of health-care systems leads to inefficient treatment, especially for elderly people with cognitive impairment. The transition from hospital care to primary care is insufficiently coordinated, and communication between health-care providers is often lacking. Consequences include a further deterioration of health, higher rates of hospital readmissions, and institutionalization. Models of collaborative care have shown their efficacy in primary care by improving patient-related outcomes. The main goal of this trial is to compare the effectiveness of a collaborative care model with usual care for people with cognitive impairment who have been admitted to a hospital for treatment due to a somatic illness. The aim of the intervention is to improve the continuity of treatment and care across the transition between the in-hospital and adjoining primary care sectors.
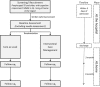
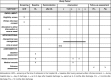
Methods/design: The trial is a longitudinal multisite randomized controlled trial with two arms (care as usual and intersectoral care management). Inclusion criteria at the time of hospital admission due to a somatic illness are age 70+ years, cognitive impairment (Mini Mental State Examination, MMSE ≤26), living at home, and written informed consent. Each participant will have a baseline assessment at the hospital and two follow-up assessments at home (3 and 12 months after discharge). The estimated sample size is n = 398 people with cognitive inmpairement plus their respective informal caregivers (where available). In the intersectoral care management group, specialized care managers will develop, implement, and monitor individualized treatment and care based on comprehensive assessments of the unmet needs of the patients and their informal caregivers. These assessments will occur at the hospital and in participants' homes. Primary outcomes are (1) activities of daily living, (2) readmission to the hospital, and (3) institutionalization. Secondary outcomes include (a) frailty, (b) delirium, (c) quality of life, (d) cognitive status, (e) behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, (f) utilization of services, and (g) informal caregiver burden.
Discussion: In the event of proving efficacy, this trial will deliver a proof of concept for implementation into routine care. The cost-effectiveness analyses as well as an independent process evaluation will increase the likelihood of meeting this goal. The trial will enable an in-depth analysis of mediating and moderating effects for different health outcomes at the interface between hospital care and primary care. By highlighting treatment and care, the study will provide insights into unmet needs at the time of hospital admission, and the opportunities and barriers to meeting those needs during the hospital stay and after discharge.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03359408 ; December 2, 2017.
Keywords: Care management; Case management; Cognitive impairment; Collaborative care; Dementia care; Discharge management; Health care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sachverständigenrat zur Begutachtung der Entwicklung im Gesundheitswesen im BMG . Wettbewerb an der Schnittstelle zwischen ambulanter und stationärer Gesundheitsversorgung. Bern: Huber Verlag; 2012.
-
- Schwartz FW. Bedarf und bedarfsgerechte Versorgung aus der Sicht des Sachverständigenrates. Das Gesundheitswesen. 2001;63(3):127–132. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz FW, Wille E, Fischer C, Kuhlmey A, Lauterbach K, Rosenbrock R, et al. Sachverständigenrat für die Konzertierte Aktion im Gesundheitswesen. Bedarfsgerechtigkeit und Wirtschaftlichkeit Gutachten. 2000;2001.
-
- Hibbard JH, Greene J. What the evidence shows about patient activation: better health outcomes and care experiences; fewer data on costs. Health Aff. 2013;32(2):207–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

